AI/ML Solutions
Let your business get a competitive edge by unlocking the power of AI and ML
TRUSTED BY
Our Evolution in AI, Data Science, and Intelligent Automation
At BigDataCentric, we lead the way in delivering innovative Artificial Intelligence and Data Science solutions that empower businesses to make smarter, faster decisions. What began as a vision to simplify data complexities has grown into an innovation hub specializing in AI/ML, LLMs, NLP, Chatbots, and Business Intelligence. We help startups and enterprises alike harness the power of data to automate workflows, enhance customer experiences, and drive measurable growth.
Driven by innovation and excellence, BigDataCentric blends advanced technologies with strategic insight to create solutions that deliver real impact. From building AI-driven applications and predictive analytics models to deploying intelligent chatbots and data platforms, we help organizations transform digitally and stay future-ready in a data-centric world.

Years of Experience

Developers

AI Solutions

Global Clients

Technology Expertise

AI Projects Delivered
Driving Intelligent Transformation Through Advanced AI Solutions
At BigDataCentric, we deliver a comprehensive suite of AI and data-driven services designed to help organizations innovate, automate, and scale intelligently. From predictive modeling and natural language understanding to enterprise-grade LLMs and system integration, we empower businesses to harness the full potential of Artificial Intelligence for real-world impact.

Artificial intelligence
We design and deploy intelligent AI solutions that automate processes, enhance decision-making, and unlock new business opportunities. Our experts combine advanced algorithms with deep domain knowledge to deliver custom AI applications aligned with your goals. From strategy to execution, we ensure seamless adoption of AI that drives innovation, improves accuracy, and creates measurable value across operations.
Explore Our Service
Machine Learning Development Company
Our Machine Learning services empower businesses to turn data into actionable insights. We develop models for classification, forecasting, and predictive analytics that adapt and evolve with changing trends. By leveraging supervised, unsupervised, and deep learning techniques, we help organizations anticipate outcomes, optimize workflows, and enhance efficiency across departments and industries.
Explore Our Service
Natural Language Processing
Our NLP solutions redefine how businesses understand, analyze, and communicate through language. From intelligent chatbots and document summarization to sentiment analysis and entity recognition, we enable seamless interaction between humans and machines. By extracting meaning from unstructured data, we help you enhance customer experience, automate communication, and make smarter content-driven decisions.
Explore Our Service
Large Language Model Development Services
Leverage the next generation of AI innovation with our Large Language Model development services. We fine-tune and deploy LLMs customized for your domain — enabling human-like understanding, content generation, and conversational intelligence. Whether you’re building chatbots, copilots, or enterprise assistants, our LLM solutions enhance automation, improve response accuracy, and deliver intelligent user interactions at scale.
Explore Our Service
SaaS AI Development Services
We build scalable, cloud-based AI-powered SaaS solutions tailored to your business model and customer needs. Our SaaS AI expertise enables enterprises to integrate intelligent features like predictive analytics, recommendation systems, and automation tools into their platforms. From concept to deployment, we ensure performance, scalability, and seamless integration — empowering you to deliver smarter, AI-driven digital products faster.
Explore Our Service
AI Integration and Deployment
Our AI Integration and Deployment services ensure your AI and ML models move efficiently from prototype to production. We specialize in model deployment, API integration, performance monitoring, and MLOps implementation — ensuring scalability, security, and reliability. By seamlessly integrating AI into your existing systems and workflows, we help you achieve faster time-to-value and maximize ROI from your AI investments.
Explore Our ServiceReady to Redefine Your Business with AI-Powered Innovation?
Unlock intelligent AI and ML solutions designed to revolutionize your business. We turn data into powerful insights that accelerate innovation and growth.
Words From Our Clients

I am happy to recommend BigDataCentric their app development services. They successfully developed apps for me, and I am highly satisfied with the overall outcomes. The development team has swiftly addressed the issues with responsive and effective communication to understand the requirement quickly and actively resolve the back-and-forth problems that arose. The team also displayed great expertise in fixing bugs. Whenever issues were identified, they promptly decided on them, demonstrating their technical proficiency and commitment to delivering a high-quality product.
Flavio S. (Germany)
Founder & Managing Director

I highly recommend BigDataCentric as the quality of service is wonderful. We have hired this company to develop the product based on some complex & technical issues. We get the best quality services as compared with others in the market. Huge Thanks to BigDataCentric as the team is always ready to give the solution all time.
Ayse D. (France)
Co-Founder

BigDataCentric is a pioneer in the WebRTC based project as they have fixed complicated segments of the module by fulfilling different product lines by providing 24X7 customer support. We really recommended BigDataCentric as they are able to develop products as per the module deadline and project timeline.
Justin G. (United States)
Founder & CEO

BigDataCentric is the best company that provides advanced apps and websites development services in the USA and Europe. I am a newbie to develop my app with an external team. I am really happy to work with them as I am not that much mobile apps user. Here, the team and specially the CEO of BigDataCentric helps me to let me know about the benefits of my app to generate revenue. Thanks, BigDataCentric as I like their components as Trust, Commitment, Quality and Price.
Jay M. (United States)
Founder & CEO

BigDataCentric provides the best mobile app development solutions and as a team, they are amazing to fulfil my requirements of sports mobile application. I recommend all the time BigDataCentric. Thanks!
Yousef A. (Jordan)
Challenger BH, Founder

BigDataCentric has created a portal by integrations with multiple modules including ETR functionality as per the requirement of the client. Here, the challenging part is to gather information, understand the idea and know about the scope of work in a given timeline. For that Team BDC has discussed different modules and was clear about the requirements with a deadline and developed.
Ehis E. (Canada)
Owner

Working with BigDataCentric has been next-level. They’ve built two apps and a fully automated website for us, handling every complex detail with speed and clarity. Their team is transparent, efficient, and truly listens – turning ideas into real, working solutions. Great communication, high-quality results, and affordable pricing. Highly recommended for anyone needing reliable tech partners.
Joshua M. (United Kingdom)
Owner
Innovations We’ve Delivered
Browse our portfolio to explore cutting-edge projects that bring efficiency and value to businesses.
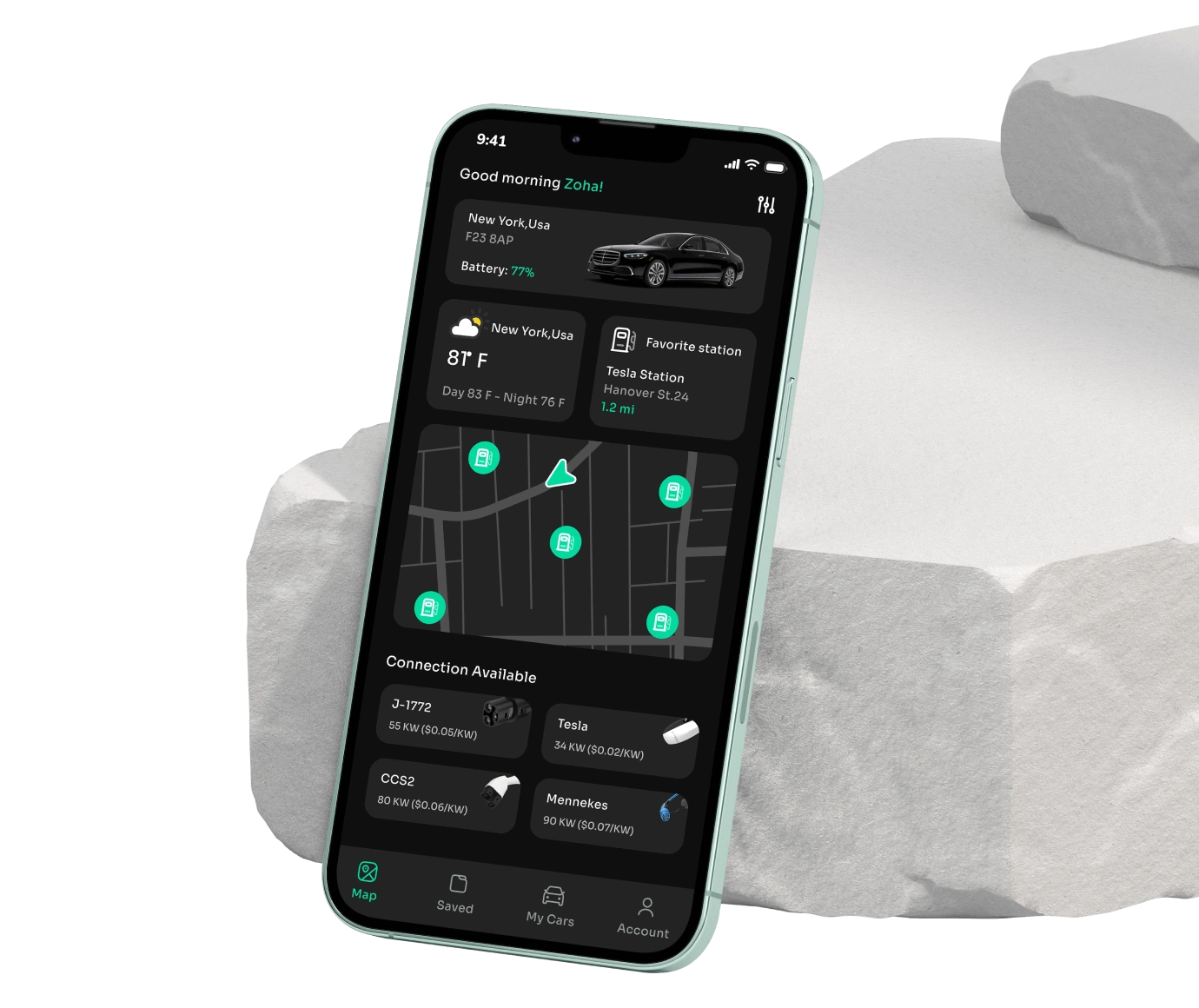
MoonEVFlex
This user-friendly app perfectly connects you to a huge network of charging stations.
TransportationIndustries We Empower with AI Innovation
At BigDataCentric, we design and deliver AI-powered, data-driven, and automation-ready solutions tailored to the unique challenges of each industry. Our expertise spans diverse sectors — empowering businesses to optimize operations, enhance decision-making, and accelerate innovation through intelligent technologies.
Technologies Stack We Use

AngularJS
Next
HTML
CSS
JavaScript
React

Angular
Vue
Node.js
Python
.NET Core
PHP
JAVA
Nest
AWS
Azure
GCP
Kubernetes
Jenkins
GitLab
GitHub
Ansible
Terraform
Azure DevOps
Splunk
Swift
Kotlin
React Native
Flutter
PWA
TensorFlow
PyTorch
Keras
Torch
SparkML
GPT
BERT
Our Proven Development Process
At BigDataCentric, we follow a structured and transparent process to deliver high-performing solutions. Every stage is designed to ensure innovation, quality, and measurable business impact.
Discovery & Insight Gathering
We begin by understanding your business goals, challenges, and data ecosystem to design the right AI-driven strategy.
Data Collection & Preparation
We gather, clean, and process high-quality data from multiple sources to build a reliable foundation for AI modeling.
Deployment & Integration
We seamlessly integrate the solution into your existing systems, ensuring smooth adoption and real-world impact.












Strategy & Planning
Our experts define project milestones, timelines, and technical frameworks to ensure smooth and efficient execution.
Model Development & Testing
Custom AI and ML models are developed and rigorously tested to ensure accuracy, scalability, and performance.
Continuous Monitoring & Support
Our team provides ongoing monitoring, updates, and optimization to keep your AI solutions performing at their best.
Our Proven Development Process
At BigDataCentric, we follow a structured and transparent process to deliver high-performing solutions.

Discovery & Insight Gathering
We begin by understanding your business goals, challenges, and data ecosystem to design the right AI-driven strategy.

Strategy & Planning
Our experts define project milestones, timelines, and technical frameworks to ensure smooth and efficient execution.

Data Collection & Preparation
We gather, clean, and process high-quality data from multiple sources to build a reliable foundation for AI modeling.

Model Development & Testing
Custom AI and ML models are developed and rigorously tested to ensure accuracy, scalability, and performance.

Deployment & Integration
We seamlessly integrate the solution into your existing systems, ensuring smooth adoption and real-world impact.

Continuous Monitoring & Support
Our team provides ongoing monitoring, updates, and optimization to keep your AI solutions performing at their best.
Build Smarter, Scalable Digital Systems
Let BigDataCentric help you turn complex challenges into seamless, impactful, and innovative solutions for your business.
Partner With Us to Drive Intelligent Business Growth
At BigDataCentric, we deliver innovative, scalable, and data-driven solutions that empower businesses to make smarter decisions, automate processes, and accelerate growth. Partner with us for AI, ML, and advanced analytics solutions designed to create real impact.

Expertise & Tailored Solutions
Our team combines deep technical expertise with industry insights to deliver solutions designed for your unique business needs. We ensure every project is customized for maximum efficiency and impact.

Proven Track Record
We have successfully partnered with startups, SMEs, and enterprises, delivering intelligent solutions that generate measurable results. Our portfolio demonstrates reliability, innovation, and consistent client satisfaction.

Flexible & Adaptive Approach
We provide scalable, adaptable AI and data-driven solutions that align with your evolving goals and workflows. Our agile approach ensures your solution grows with your business.

Collaborative Partnership
From strategy to deployment, we work closely with your team to ensure solutions are fully aligned with your vision. Collaboration and transparency are at the heart of our process.

Future-Ready Innovation
We leverage the latest technologies in AI, ML, NLP, and LLMs to keep your business ahead of the curve. Our forward-thinking solutions prepare you for emerging trends and evolving market needs.

End-to-End Support
Beyond deployment, we offer ongoing monitoring, optimization, and maintenance to ensure your AI solutions continue to deliver value. Our support guarantees performance, reliability, and continuous improvement over time.
Top Blogs
Stay informed and inspired with our latest insights, trends, and expert perspectives across industries.
Get in Touch to Discuss Your Ideas
Get all-in-one development solutions and services related to your inquiries. Fill up the form below and one of our representatives will contact to you shortly.