Big Data Governance Explained for Modern Data Management

Blog Summary:
This blog explains how organizations can manage large, complex data environments in a structured, reliable way. It covers key concepts, business benefits, core governance elements, and real-world industry use cases. The content also outlines best practices for building a scalable governance approach. It concludes with guidance on developing a future-ready strategy that supports secure data usage and confident decision-making.
As organizations generate and consume data at unprecedented scale, how this data is managed, protected, and made usable has become a critical business concern.
Modern enterprises no longer deal only with structured databases but with vast volumes of diverse, fast-moving, and distributed data coming from multiple sources. Without a disciplined approach, this data can quickly become a liability rather than an asset.
This is where Big Data Governance plays a defining role. It provides a structured way to ensure that data across the organization remains accurate, secure, compliant, and accessible to the right people at the right time. Rather than restricting data usage, governance brings clarity and control, helping businesses balance innovation with accountability.
In highly regulated and data-driven environments, strong governance practices are no longer optional. They influence how confidently organizations can make decisions, meet regulatory expectations, reduce operational risks, and scale analytics initiatives.
A well-defined governance approach also lays the foundation for trust in data, which is essential for long-term digital and analytical maturity.
In the sections that follow, we will explore what data governance truly means in the context of big data, its business value, core components, industry use cases, and the practices needed to build a future-ready governance strategy.
Understanding Big Data Governance
Big data governance defines how large, diverse datasets are managed, controlled, and used across an organization. As data volumes increase and sources become more complex, governance ensures that information remains accurate, consistent, and trustworthy.
It provides clarity on how data should be handled from ingestion to consumption, regardless of where it resides.
In modern data ecosystems, governance goes beyond basic policies. A well-structured data governance framework helps organizations standardize definitions, manage access, and maintain quality across data lakes, cloud platforms, and analytics systems.
Rather than limiting access, it enables secure, confident use of data by establishing clear rules and responsibilities.
Most importantly, big data governance is not only about technology. It involves people, processes, and accountability working together. When supported by a clear data governance model and aligned with business goals, it becomes a foundation for reliable decision-making, regulatory compliance, and scalable data initiatives.
What are the Business Benefits of Data Governance?

Strong data governance directly affects how effectively an organization uses its data while minimizing risk. By setting clear rules around ownership, access, and usage, governance helps businesses turn growing data volumes into reliable, decision-ready assets.
The benefits extend beyond compliance to include operational efficiency, transparency, and smarter data use across teams.
Enhanced Security & Privacy
Data governance establishes clear controls over who can access sensitive data and under what conditions. By applying consistent classification, access policies, and monitoring practices, organizations can reduce the risk of breaches, misuse, and unauthorized exposure of critical information.
Faster, Better Decision-Making
When data quality and consistency are governed properly, teams spend less time validating data and more time analyzing it. Trusted data enables faster insights, reduces conflicting reports, and supports confident decision-making at both operational and strategic levels.
Greater Transparency & Accountability
Governance defines ownership and accountability for data assets, clarifying who is responsible for accuracy, updates, and access approvals. This transparency improves collaboration between teams and reduces ambiguity in data-related decisions.
Data Democratization with Control
A well-designed data governance system allows broader data access without compromising security. Business users can discover and use data independently, while governance policies ensure usage remains compliant and aligned with organizational standards.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Standardized data management processes reduce duplication, rework, and manual corrections. This improves overall efficiency by streamlining how data is collected, maintained, and shared across departments.
Regulatory Compliance
Governance helps organizations meet regulatory and industry-specific requirements by enforcing data retention, privacy, and auditability standards. With clear documentation and controls in place, compliance becomes proactive rather than reactive.
Build a Reliable Big Data Governance Framework
Create consistency and accountability across your data environment with a structured big data governance strategy tailored to your business needs.
Key Elements of Data Governance
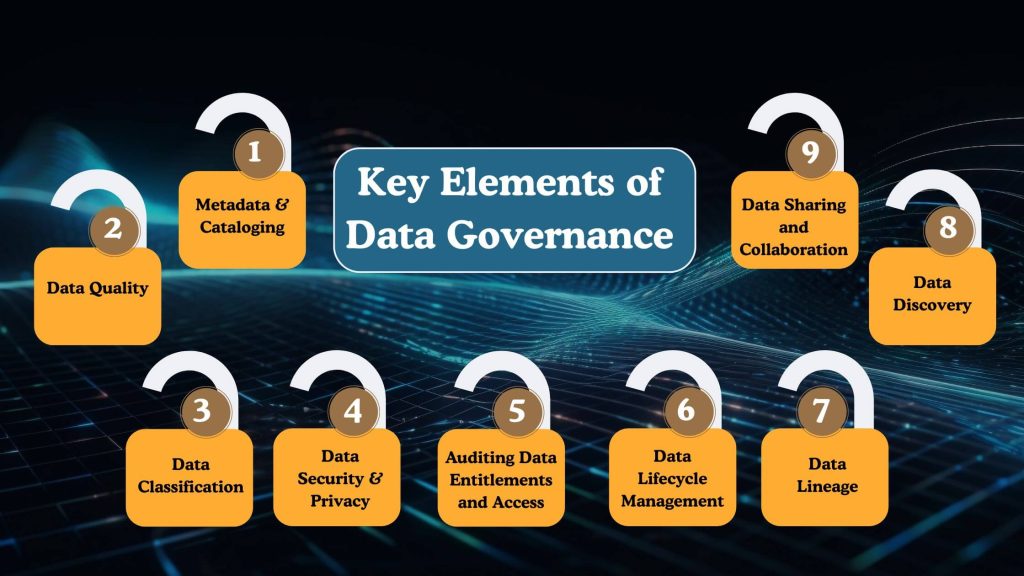
A strong governance foundation is built on multiple interconnected elements that work together to maintain data reliability, security, and usability. These elements ensure that data is properly organized, protected, traceable, and accessible throughout its lifecycle, even as data environments scale and diversify.
Metadata & Cataloging
Metadata and cataloging provide context to data by defining what data exists, where it comes from, and how it can be used. A centralized catalog helps users quickly discover relevant datasets, understand definitions, and avoid duplication or misuse.
Data Quality
Data quality focuses on maintaining the accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness of data. Governance processes help identify errors, standardize formats, and enforce quality checks so that data remains reliable for analytics and reporting.
Data Classification
Classification involves categorizing data based on sensitivity, usage, and regulatory requirements. This makes it easier to apply appropriate access controls, security measures, and retention policies across data types.
Data Security & Privacy
Big data security and privacy ensure that sensitive and regulated data is protected from unauthorized access. Governance defines access rules, encryption standards, and compliance measures that safeguard data while enabling legitimate use.
Auditing Data Entitlements and Access
Auditing tracks who has access to data and how it is being used. Regular audits help organizations detect misuse, validate permissions, and maintain accountability across teams and systems.
Data Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle management governs how data is created, stored, archived, and retired. Clear lifecycle rules reduce storage costs, minimize risk, and ensure compliance with retention and deletion requirements.
Data Lineage
Data lineage provides visibility into how data flows across systems, transformations, and reports. This traceability helps teams understand data dependencies, troubleshoot issues, and maintain trust in analytics outputs.
Data Discovery
Discovery enables users to easily find and evaluate data assets. Governed discovery ensures that users access approved, well-documented data rather than relying on unverified or duplicate sources.
Data Sharing and Collaboration
Governance enables secure, controlled data sharing across teams and departments. Defined policies and standards encourage collaboration while ensuring data is used responsibly and consistently.
What Should an Ideal Big Data Governance Solution Include?
An effective governance solution should support control without limiting usability. It must scale with growing data volumes, adapt to diverse data environments, and align closely with business priorities while maintaining consistency and compliance.
Clear Policies & Standards
Clear policies define how data should be created, accessed, used, and retained. They remove ambiguity by setting organization-wide standards. This ensures consistent handling of information across teams and big data platforms.
Defined Roles & Ownership
Well-defined roles establish accountability for data assets. Owners and stewards are responsible for quality, access approvals, and issue resolution. This prevents confusion and improves governance execution.
Data Discovery & Cataloging
A strong discovery and cataloging capability helps users quickly find trusted data. It provides context through metadata, definitions, and ownership details. This reduces dependency on manual data searches.
Automation
Automation reduces manual effort required to enforce governance rules. It helps apply policies, monitor compliance, and manage access at scale. This makes governance more efficient and sustainable.
Business Alignment
Governance should align with business goals rather than operate in isolation. Policies and controls must support analytics, reporting, and innovation needs. This ensures governance delivers measurable business value.
Open Marketplace for Data, Analytics and AI
An open marketplace enables governed sharing of data and analytical assets. Users can access approved datasets, models, and insights in one place. This promotes reuse while maintaining control and compliance.
Design a Scalable Big Data Governance Strategy
Ensure trusted data usage across teams and platforms with governance models built for growing and distributed data environments.
Industry-Wise Use Cases of Big Data Governance
Different industries face unique data challenges driven by regulations, scale, and operational complexity. A well-implemented governance approach helps organizations manage these challenges and enable secure, responsible data use across business functions.
Finance
- Fraud Detection & Risk Management
Governed data ensures transaction and behavioral data is accurate, timely, and traceable. This improves fraud detection models and supports consistent risk assessments. Clear access controls also protect sensitive financial information.
- Customer Personalization
Data governance helps financial institutions unify customer data from multiple sources. With standardized definitions and quality controls, personalization efforts become more reliable. This leads to relevant offers without compromising data privacy.
- Regulatory Compliance
Strict governance policies support compliance with financial regulations and audits. Data lineage and access logs provide transparency into how data is used. This reduces compliance risk and regulatory penalties.
Healthcare
- Patient Data Protection
Governance ensures patient data is classified, secured, and accessed only by authorized users. Privacy controls and audit trails support compliance with healthcare regulations. This builds trust while protecting sensitive medical information.
- Improved Patient Outcomes
High-quality and well-governed data enable accurate clinical insights. Healthcare providers can rely on consistent data for diagnosis and treatment planning. This supports better, data-driven patient care.
- Operational Efficiency
Governance reduces data duplication across departments and systems. Streamlined access to trusted data improves coordination between clinical and administrative teams. This leads to more efficient healthcare operations.
Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance
Governed machine and sensor data ensures accuracy and consistency across systems. Reliable data supports predictive maintenance initiatives. This helps reduce downtime and equipment failures.
- Process Optimization
Data governance enables manufacturers to analyze production data with confidence. Standardized data improves visibility into processes and bottlenecks. This supports continuous improvement and cost reduction.
Government & Public Sector
- Urban Planning
Governed data from multiple public sources improves planning decisions. Clear ownership and quality standards ensure data reliability. This supports smarter infrastructure and city planning initiatives.
- Crime Prevention
Data governance helps law enforcement agencies manage and analyze sensitive data responsibly. Controlled access and auditability improve accountability. This enhances crime analysis without compromising privacy.
- Public Service Improvement
Governed data enables better service delivery and performance measurement. Agencies can share data securely across departments. This leads to more transparent and efficient public services.
5 Data Governance Best Practices

Effective governance is not built overnight. It evolves through consistent practices that balance control, usability, and business priorities.
The following best practices help organizations create a governance approach that is practical, scalable, and results-driven.
Align with Business Goals & Get Executive Buy-In
Governance initiatives succeed when they are tied directly to business objectives. Executive sponsorship ensures priorities are clear and governance decisions are supported across teams.
This alignment helps governance deliver measurable value rather than operating as a standalone effort.
Define Clear Roles & Accountability
Clearly defined roles eliminate confusion around data ownership and responsibility. Data owners, stewards, and custodians must understand their specific duties.
This accountability ensures data quality, access control, and issue resolution are handled consistently.
Create Practical Policies & Frameworks
Policies should be actionable and easy to follow, not overly complex or theoretical. A well-structured data governance framework provides guidance without slowing down operations. Practical rules encourage adoption and long-term sustainability.
Automate & Use Technology
Automation helps enforce governance rules at scale. Tools can support monitoring, access control, data classification, and quality checks. This reduces manual effort and ensures consistency across growing data environments.
You Might Also Like
Monitor, Measure & Iterate
Governance should be continuously evaluated and improved. Tracking metrics such as data quality, access issues, and compliance gaps helps identify weaknesses. Regular iteration ensures governance keeps pace with changing business and regulatory needs.
Future-Ready Big Data Governance Strategy
As data ecosystems continue to evolve, governance strategies must be designed with flexibility and scalability in mind. Organizations need to prepare for growing data volumes, expanding cloud adoption, and increased regulatory scrutiny without slowing down innovation. A future-ready approach focuses on adaptability rather than rigid controls.
Modern governance strategies emphasize integration with data platforms, analytics tools, and business workflows. This ensures governance becomes part of everyday data usage rather than a separate compliance layer.
By embedding governance into data operations, organizations can maintain consistency while enabling faster access to trusted data.
Equally important is continuous improvement. Governance strategies should be regularly reviewed to reflect new regulations, technologies, and business goals.
When supported by the right processes and ownership, a future-ready governance approach helps organizations stay compliant, competitive, and confident in their data-driven initiatives.
Still Struggling With Data Control and Compliance?
Adopt a well-defined governance approach to improve visibility, security, and accountability.
Conclusion
As organizations continue to rely on data for decision-making, compliance, and innovation, a structured governance approach is essential. Big Data Governance brings consistency, security, and accountability to complex data environments, helping businesses manage risk while improving trust in data.
When supported by the right policies, processes, and technology, governance turns data into a reliable business asset rather than a challenge.
This is where BigDataCentric plays a meaningful role. With strong expertise in data engineering, analytics, and enterprise data management, BigDataCentric helps organizations design and implement governance strategies aligned with real business needs.
From building scalable data platforms to enabling secure data access and quality management, the focus remains on practical, outcome-driven governance.
By combining technical expertise with a business-first mindset, organizations can establish governance models that support growth, regulatory readiness, and long-term data maturity. A well-executed governance strategy not only protects data but also empowers teams to use it confidently and responsibly.
FAQs
-
How does data governance compare to master data management (MDM)?
Data governance defines the policies, roles, and controls for managing all enterprise data. Master data management focuses on creating and maintaining consistent, authoritative records for key business entities, such as customers and products.
-
What are the 5 pillars of data governance?
The five pillars are data quality, data security, data privacy, data ownership, and data compliance. Together, they ensure that data is accurate, protected, accountable, and used in accordance with regulations and business rules.
-
What are the 8 principles of data governance?
The eight principles include accountability, transparency, integrity, auditability, standardization, compliance, accessibility, and security. These principles guide how data is managed, controlled, and trusted across the organization.
-
What tools are used for data governance?
Common data governance tools include data catalogs, metadata management platforms, data quality tools, access control solutions, and monitoring systems. These tools help enforce policies and maintain visibility across data environments.
-
What are the 5 V's in big data?
The five V’s are volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value. They describe the scale, speed, diversity, reliability, and business importance of big data.

Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
Toggle- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611
