How Does Data Science Automation Transform Analytics Workflows?

Blog Summary:
Data science automation helps organizations streamline repetitive tasks across data pipelines, analytics workflows, and model operations. It enables teams to improve efficiency, maintain consistency, and scale analytics initiatives with minimal manual effort. By automating core processes, businesses can accelerate insights while reducing errors and operational overhead. The blog explores key benefits, essential processes, popular tools, and best practices for implementing automation effectively.
Modern businesses generate data at a pace that manual processes cannot keep up with. From collecting raw information to building predictive models, data teams often spend more time managing workflows than extracting meaningful insights. This growing complexity has pushed organizations to rethink how data-driven work is executed across the entire lifecycle.
Data Science Automation addresses this challenge by reducing repetitive, manual tasks across data pipelines, analytics workflows, and model operations. Instead of relying on fragmented processes and constant human intervention, organizations can streamline how data is prepared, analyzed, and operationalized. This shift allows teams to focus on decision-making and innovation rather than operational overhead.
As data volumes grow and use cases expand across departments, automation becomes essential for maintaining speed, accuracy, and consistency. Businesses exploring the future of data-driven decision-making are increasingly aligning automation with broader analytics strategies, much as modern enterprises are redefining the future of data science through scalable, efficient practices.
In this blog, we explore what data science automation really means, why it matters for businesses, the key processes and data science tools involved, and how organizations can implement it effectively to achieve faster, more reliable outcomes.
Key Statistics on Data Science Automation
Automation Potential:
According to PwC, nearly 45% of repetitive data-related tasks are expected to be automated by 2025. Additionally, studies suggest that nearly 90% of new data science initiatives will include automated machine learning (AutoML) in their workflows during the same period.
Efficiency Gains:
Data preparation often takes up to 80% of a data professional’s time. By introducing automation at this stage, organizations can significantly cut down this effort—by as much as 80%—allowing teams to focus more on advanced analysis, strategic alignment, and meaningful interpretation of insights.
Market Expansion:
The global market for data science platforms is projected to grow rapidly. Some estimates indicate it could reach approximately $470.92 billion by 2030, driven by the growing adoption of automation and intelligent analytics.
Adoption Across Industries:
- Finance: Around 61% of financial organizations have already adopted robotic process automation and machine learning to strengthen risk management and regulatory compliance.
- Healthcare: Nearly 89% of healthcare leaders have invested in advanced analytics and intelligent systems to improve clinical and operational outcomes.
- Manufacturing: About 40% of manufacturing enterprises are leveraging big data analytics to enhance supply chain efficiency and operational performance.
What is Data Science Automation?
Data science automation is the practice of using automated tools and workflows to handle repetitive, manual tasks throughout the data science lifecycle. These tasks include data collection, preparation, feature creation, model training, evaluation, and deployment.
Rather than replacing human expertise, automation supports data teams by minimizing operational effort and reducing dependency on manual execution.
In traditional workflows, data scientists often spend significant time managing data pipelines and resolving process inconsistencies. Automation standardizes and automates these workflows, ensuring processes run the same way every time.
This improves data quality, reduces errors, and allows teams to maintain consistency across experiments and production environments.
Data Science Automation also makes it easier for organizations to scale analytics initiatives as data volumes and business requirements grow. Automated pipelines can support multiple datasets and models simultaneously without increasing complexity.
As a result, businesses can move faster from experimentation to deployment while maintaining reliable, efficient, data-driven operations.
Why is Data Science Automation important for Businesses?
As organizations rely more heavily on data to guide decisions, the speed and accuracy of analytics become critical. Manual data science workflows often slow down this process, creating bottlenecks in data preparation, model development, and deployment.
Automation helps businesses reduce these delays by ensuring data pipelines and analytical processes run consistently without constant human intervention.
Data science automation is especially important for maintaining quality and reliability at scale. When multiple teams work with growing datasets, even small inconsistencies can lead to flawed insights.
Automated workflows standardize how data is processed and models are built, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of errors across business-critical use cases.
From a strategic perspective, automation allows businesses to move beyond experimentation and toward operational analytics. Insights can be delivered faster, models updated more frequently, and outcomes aligned more closely with business objectives.
This shift reflects how many organizations are evolving their analytics practices to support long-term growth and innovation, similar to broader trends shaping the future of data science across industries.
Build Scalable Analytics with Automation
Enable faster insights and consistent performance through Data Science Automation aligned with your business goals and data strategy.
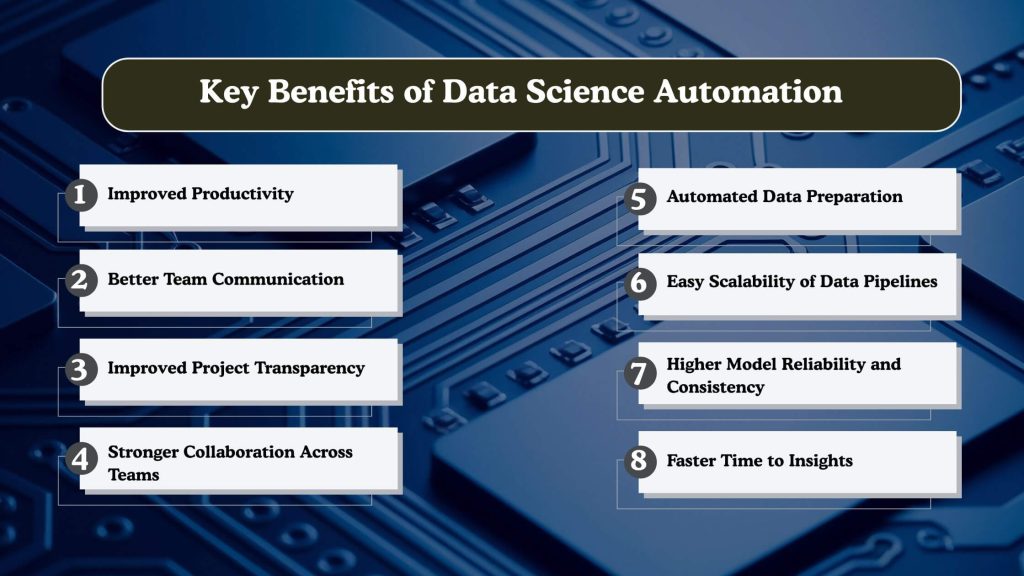
Key Benefits of Data Science Automation
As data ecosystems grow more complex, managing analytics workflows manually becomes inefficient and error-prone. Automating data science workflows helps organizations streamline operations, reduce delays, and maintain consistency across projects.
These benefits collectively enable teams to deliver reliable insights while keeping pace with evolving business needs.
Improved Productivity
Automation significantly reduces time spent on repetitive tasks, including data cleaning, pipeline execution, and model retraining. By eliminating manual intervention in routine processes, data teams can focus more on advanced analysis, experimentation, and solving business problems that require human judgment.
Better Team Communication
Automated workflows create standardized processes that are easier for teams to understand and follow. When pipelines, models, and outputs are consistently structured, communication gaps between data engineers, analysts, and stakeholders are minimized, leading to clearer expectations and smoother handoffs.
Improved Project Transparency
With automation, every step of the data science process becomes traceable and measurable. Teams gain better visibility into pipeline status, model performance, and data dependencies, making it easier to track progress, identify issues early, and ensure accountability throughout the project lifecycle.
Stronger Collaboration Across Teams
Automation supports collaboration by providing shared frameworks and repeatable workflows. Multiple teams can work on the same datasets or models without conflicts, ensuring alignment across departments and reducing friction during development and deployment stages.
Automated Data Preparation
Data preparation is one of the most time-consuming phases in analytics. Automating data ingestion, cleansing, and transformation ensures data is consistently prepared for analysis, improves data quality, and reduces delays caused by manual preprocessing.
Easy Scalability of Data Pipelines
As data volumes and use cases grow, automation allows pipelines to scale without proportional increases in manual effort. Automated pipelines can handle larger datasets, additional sources, and higher processing frequency while maintaining performance and reliability.
Higher Model Reliability and Consistency
Automated model training, validation, and deployment reduce variability caused by manual execution. Standardized workflows ensure models are built and evaluated using consistent criteria, improving reliability and enabling teams to trust outputs used for decision-making.
Faster Time to Insights
By streamlining the entire data science lifecycle, automation shortens the gap between data collection and actionable insights. Faster execution of pipelines and models allows businesses to respond quickly to market changes, customer behavior, and operational challenges.
You Might Also Like:
Core Data Science Automation Processes

Data science automation relies on a set of structured processes that work together to ensure data flows smoothly from raw sources to production-ready models.
Automating these processes helps organizations reduce manual dependencies, maintain consistency, and scale analytics initiatives with confidence. Each stage plays a critical role in building reliable and efficient data-driven systems.
Data Ingestion & Collection
This process focuses on automatically collecting data from multiple sources, including databases, applications, APIs, and third-party platforms. Automation ensures data is collected at regular intervals or in real time, reducing delays and minimizing the risk of missing or inconsistent inputs.
Data Preparation & Cleaning
Automated data preparation handles tasks such as removing duplicates, handling missing values, and standardizing data formats. By applying consistent rules across datasets, organizations can improve data quality while significantly reducing the manual effort required to make data analysis-ready.
Data Integration
Data integration automation combines information from different systems into a unified view. This ensures datasets are aligned, reduces data silos, and enables analytics teams to work with comprehensive, consistent data across business functions.
Feature Engineering
Automation in feature engineering enables efficient generation, transformation, and selection of relevant features. By standardizing feature creation, teams can reduce time spent on experimentation and ensure models are built using reliable, reusable inputs.
Model Training & Tuning
Automated model training enables systems to run multiple experiments, adjust parameters, and identify optimal configurations without manual intervention. This improves efficiency and enables teams to develop robust models more quickly.
Model Evaluation & Validation
Automation ensures models are consistently evaluated against predefined metrics and validation criteria. This helps identify performance issues early and ensures only reliable models move forward into production environments.
Model Deployment
Automated deployment streamlines moving models into production systems. It reduces errors, shortens release cycles, and ensures models are integrated seamlessly into business applications.
Monitoring & Retraining
Once deployed, automated monitoring tracks model performance, data drift, and system behavior over time. When performance declines, retraining workflows can be triggered automatically to keep models accurate and relevant.
Start Your Automation Journey Today
Simplify complex analytics workflows and scale data-driven decisions using Data Science Automation built for modern businesses.
Popular Tools Used for Data Science Automation
Implementing automation across data science workflows requires reliable tools that efficiently manage pipelines, models, and data dependencies. These tools help standardize processes, reduce manual intervention, and ensure scalability as analytics initiatives grow.
Below are some widely used platforms that support automated data science operations-
Apache Airflow
Apache Airflow is commonly used to orchestrate and schedule complex data workflows. It allows teams to define automated pipelines as code, manage task dependencies, and monitor execution in real time. This makes it easier to maintain consistent and repeatable data processes across projects.
MLflow
MLflow focuses on managing the machine learning lifecycle, including experiment tracking, model versioning, and deployment. By automating these aspects, teams can compare model performance, reproduce experiments, and move models into production with greater reliability.
Kubeflow
Kubeflow is designed to run machine learning workflows on Kubernetes. It enables automation of model training, tuning, and deployment at scale, making it suitable for organizations managing multiple models and large datasets across distributed environments.
Data Version Control (DVC)
DVC automates version control for datasets, models, and experiments. By tracking changes alongside code, it ensures reproducibility and consistency, allowing teams to collaborate more effectively without losing control over data and model versions.
TensorFlow Extended (TFX)
TFX provides an end-to-end platform for building and deploying production-ready machine learning pipelines. It automates tasks such as data validation, model training, and performance monitoring, ensuring models meet quality standards before and after deployment.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Science Automation
Implementing automation successfully requires more than just tools—it needs a thoughtful, phased approach that aligns with business goals and team workflows.
The following best practices help ensure automation delivers consistent value while remaining flexible and scalable over time.
Automate Data Pipelines Early
Starting automation at the data pipeline level helps eliminate manual bottlenecks from the beginning. Early automation ensures data flows consistently from source to analysis, reducing delays and minimizing errors caused by ad-hoc handling. This also provides a strong foundation for downstream analytics and modeling.
Enable Automated Model Testing
Automated testing helps validate model performance before deployment and after updates. By consistently checking accuracy, bias, and performance metrics, teams can catch issues early. This approach reduces deployment risks and ensures models meet predefined quality standards.
Focus on Model Monitoring Metrics
Once models are live, continuous monitoring is essential. Automated tracking of performance metrics, data drift, and prediction quality helps teams detect degradation early. This ensures models remain reliable as data patterns and business conditions change.
Reduce Manual Effort with Automation
Automation should target repetitive and time-consuming tasks first. By minimizing manual interventions in data preparation, training, and deployment, teams can focus on analysis and strategic improvements. This improves efficiency without compromising control.
Integrate Security into Pipelines
Security should be embedded directly into automated workflows. Automating access controls, data validation, and compliance checks helps protect sensitive data while ensuring governance requirements are consistently met across pipelines.
Use Pipeline-as-Code Approach
Defining pipelines as code improves transparency and reproducibility. It allows teams to track changes, collaborate effectively, and roll back updates when needed. This approach also supports version control and consistent execution across environments.
Enable Self-Service Data Workflows
Self-service automation empowers analysts and data teams to run workflows without constant engineering support. This reduces dependency bottlenecks while maintaining standardized processes, enabling faster experimentation and decision-making.
Automate Changes Incrementally
Rather than automating everything at once, a phased approach reduces risk. Incremental automation allows teams to test, learn, and refine workflows while maintaining system stability and business continuity.
Commit to Continuous Model Improvement
Automation should support ongoing model refinement, not one-time deployment. Regular retraining and evaluation help models stay aligned with evolving data and business needs, ensuring long-term effectiveness.
Maintain Clear Documentation
Clear documentation is critical for automated systems. It helps teams understand workflows, dependencies, and decision logic, making it easier to onboard new members, troubleshoot issues, and maintain long-term consistency.
Start Your Data Science Automation Journey with BigDataCentric
Building reliable and scalable automated data science workflows requires the right mix of strategy, technology, and execution expertise. At BigDataCentric, we help organizations design automation frameworks that align with their data maturity, business objectives, and existing analytics ecosystems.
From streamlining data pipelines to operationalizing models, our approach focuses on delivering consistency and measurable outcomes.
Our team works closely with businesses to identify automation opportunities across the data lifecycle, ensuring processes are optimized without adding unnecessary complexity.
By applying proven practices from modern analytics and data engineering, we enable teams to reduce manual effort while improving accuracy and speed across projects.
Whether you are starting with automation or looking to optimize existing workflows, BigDataCentric supports end-to-end implementation with a focus on scalability, governance, and long-term value.
This structured approach helps organizations turn data initiatives into dependable, production-ready solutions.
Looking to Streamline Your Data Science Processes?
Reduce manual workloads and improve analytics efficiency with Data Science Automation designed for scalable and reliable outcomes.
Conclusion
As data volumes and analytical demands continue to grow, manual workflows are no longer sustainable for modern businesses. Data Science solutions and Automation enable organizations to standardize processes, improve reliability, and accelerate the delivery of insights across teams.
By automating key stages of the data science lifecycle, businesses can reduce operational overhead while maintaining accuracy and scalability.
Adopting automation is not just a technical upgrade but also a strategic move toward more efficient, resilient data-driven decision-making.
With the right tools, practices, and implementation approach, organizations can build analytics systems that evolve with changing data and business needs, ensuring long-term impact and competitive advantage.
FAQs
-
Can automated data science pipelines scale with growing data volumes?
Yes, automated pipelines are designed to handle increasing data volumes by dynamically managing data ingestion, processing, and execution. They scale without requiring proportional manual effort or team expansion.
-
Can data science automation integrate with existing business systems?
Data science automation can integrate seamlessly with existing systems such as CRMs, ERPs, data warehouses, and cloud platforms. APIs and connectors enable smooth data exchange without disrupting current operations.
-
How are model updates handled in automated workflows?
Model updates are managed through automated retraining and validation processes triggered by performance metrics or data changes. This ensures models remain accurate and relevant over time.
-
Is data science automation suitable for industry-specific use cases?
Yes, automation frameworks can be customized to meet industry-specific requirements, including regulatory, operational, and data constraints. This makes them applicable across sectors such as finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail.
-
Can data science automation be implemented incrementally?
Automation is often introduced in phases, starting with high-impact tasks like data preparation or model training. This incremental approach reduces risk and allows teams to adapt workflows gradually.

Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
Toggle- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




