DevOps Automation: Meaning, Benefits, Processes, and Best Practices

Blog Summary:
This guide covers how DevOps automation streamlines software delivery through automated infrastructure, testing, and deployment workflows. It explains how automation reduces manual effort and improves system reliability. The guide also highlights key processes, tools, and best practices that support scalable delivery. Together, these approaches help teams release software faster and more consistently.
Modern software teams are under constant pressure to release faster without breaking stability. Manual processes, disconnected tools, and slow handoffs often become bottlenecks that impact delivery timelines and system reliability. This is where DevOps Automation becomes essential, helping teams shift from reactive operations to predictable, repeatable workflows.
By automating infrastructure provisioning, testing, deployment, and monitoring, organizations can reduce human error and maintain consistent environments across development, testing, and production. Automation also allows teams to focus more on innovation rather than routine operational tasks that slow progress.
As cloud adoption, microservices, and continuous delivery models grow, automation is no longer optional. It plays a critical role in aligning development and operations teams, enabling faster releases, improved collaboration, and measurable business outcomes.
Many organizations exploring cloud and DevOps maturity already view automation as foundational to scalable, resilient systems, much as infrastructure automation supports modern cloud workflows.
What is DevOps Automation?
DevOps Automation refers to the use of automated tools and workflows to manage repetitive and manual tasks across the software development and IT operations lifecycle.
It replaces time-consuming manual processes with predefined workflows that consistently handle infrastructure provisioning, application deployment, testing, monitoring, and system maintenance.
Instead of relying on manual scripts or ad-hoc actions, automation standardizes how environments are created, configured, and updated. This ensures that development, testing, and production systems behave consistently, reducing errors caused by configuration drift. Many teams adopt automation alongside practices such as continuous integration and delivery, in which code changes flow through pipelines with minimal manual intervention.
At its core, DevOps automation connects people, processes, and tools into a unified workflow. Developers can push code confidently, operations teams can manage infrastructure predictably, and releases become faster and more reliable.
Automation also plays a key role in cloud-native environments, where dynamic infrastructure and frequent releases demand speed and consistency, much as infrastructure automation supports scalable DevOps pipelines.
Why DevOps Automation is Important for Businesses?
Businesses today operate in highly competitive and fast-changing digital environments. Releasing features slowly or dealing with frequent production issues can directly impact customer experience and revenue.
DevOps Automation helps organizations overcome these challenges by creating reliable, repeatable delivery processes that enable rapid innovation without sacrificing stability.
Automation reduces dependency on manual interventions, which are often error-prone and difficult to scale. When deployments, testing, and infrastructure updates are automated, teams can release updates more frequently while maintaining consistent quality.
This consistency is especially valuable for growing businesses managing multiple environments, cloud platforms, or distributed teams.
From a business perspective, automation improves operational efficiency and cost control. Faster releases mean quicker user feedback, while fewer incidents reduce downtime and support costs. Automation also enables better alignment between development and operations teams, allowing them to work toward shared goals rather than managing handoffs.
For organizations investing in cloud adoption and modern delivery models, automation becomes a strategic enabler for long-term scalability and resilience.
Benefits of DevOps Automation
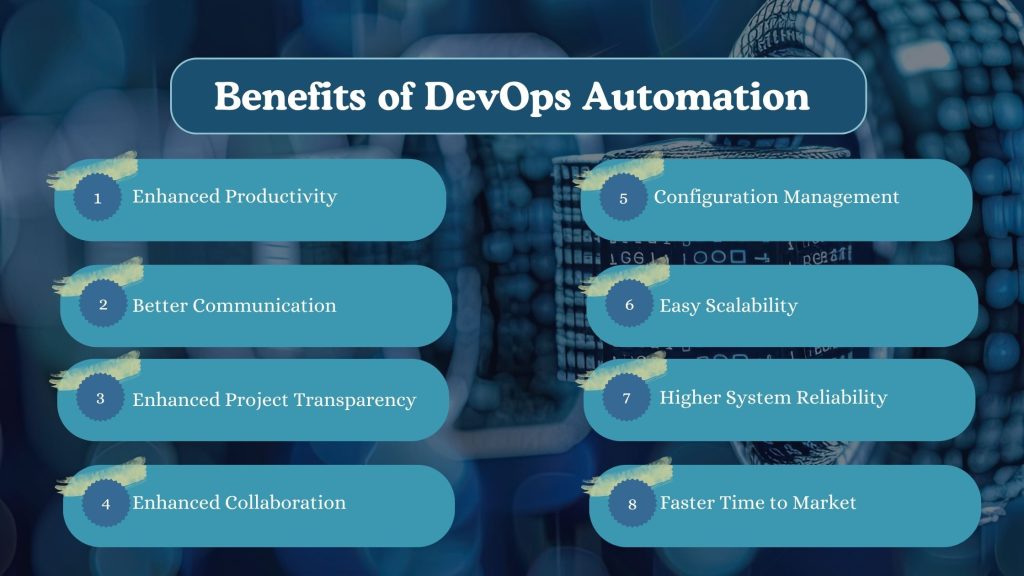
DevOps automation delivers measurable value across teams, systems, and business outcomes. By removing repetitive manual work and standardizing workflows, organizations gain speed, consistency, and better control over their delivery pipelines.
Below are the key benefits that directly impact day-to-day operations and long-term scalability –
Enhanced Productivity
Automation frees teams from routine tasks like manual deployments, environment setup, and repetitive testing. Engineers can focus on building features and improving systems rather than fixing avoidable issues.
As workflows become repeatable, overall output increases without adding operational overhead.
Better Communication
Automated pipelines create shared visibility across development and operations teams. Everyone works from the same process, reducing misunderstandings caused by handoffs or undocumented steps.
This clarity helps teams coordinate releases more effectively and respond faster to changes.
Enhanced Project Transparency
With automation in place, every change is tracked through pipelines, logs, and dashboards. Teams can see where a build stands, why a deployment failed, or what changed between releases. This transparency supports faster decision-making and easier audits.
Enhanced Collaboration
Automation encourages teams to work together on shared pipelines and infrastructure definitions. Developers, testers, and operations teams collaborate earlier in the lifecycle, reducing late-stage surprises and improving overall delivery quality.
Configuration Management
Automated configuration management ensures environments remain consistent across development, testing, and production. It minimizes configuration drift and reduces incidents caused by mismatched system settings, a common challenge in growing cloud environments.
Easy Scalability
Automated infrastructure and deployment workflows allow systems to scale up or down without manual intervention. This is especially valuable for cloud-based applications where demand can change rapidly, and resources must adapt in real time.
Higher System Reliability
Standardized automation reduces human error during deployments and system updates. Reliable rollback mechanisms, automated checks, and consistent configurations lead to more stable applications and fewer production incidents.
Faster Time to Market
When build, test, and release cycles are automated, new features reach users more quickly. Shorter release cycles also allow businesses to gather feedback sooner and adapt faster to market demands, reinforcing the business value of DevOps automation initiatives.
Ready to Automate Your DevOps?
Improve release speed, reliability, and scalability with end-to-end DevOps automation services built for modern teams.
DevOps Automation Processes
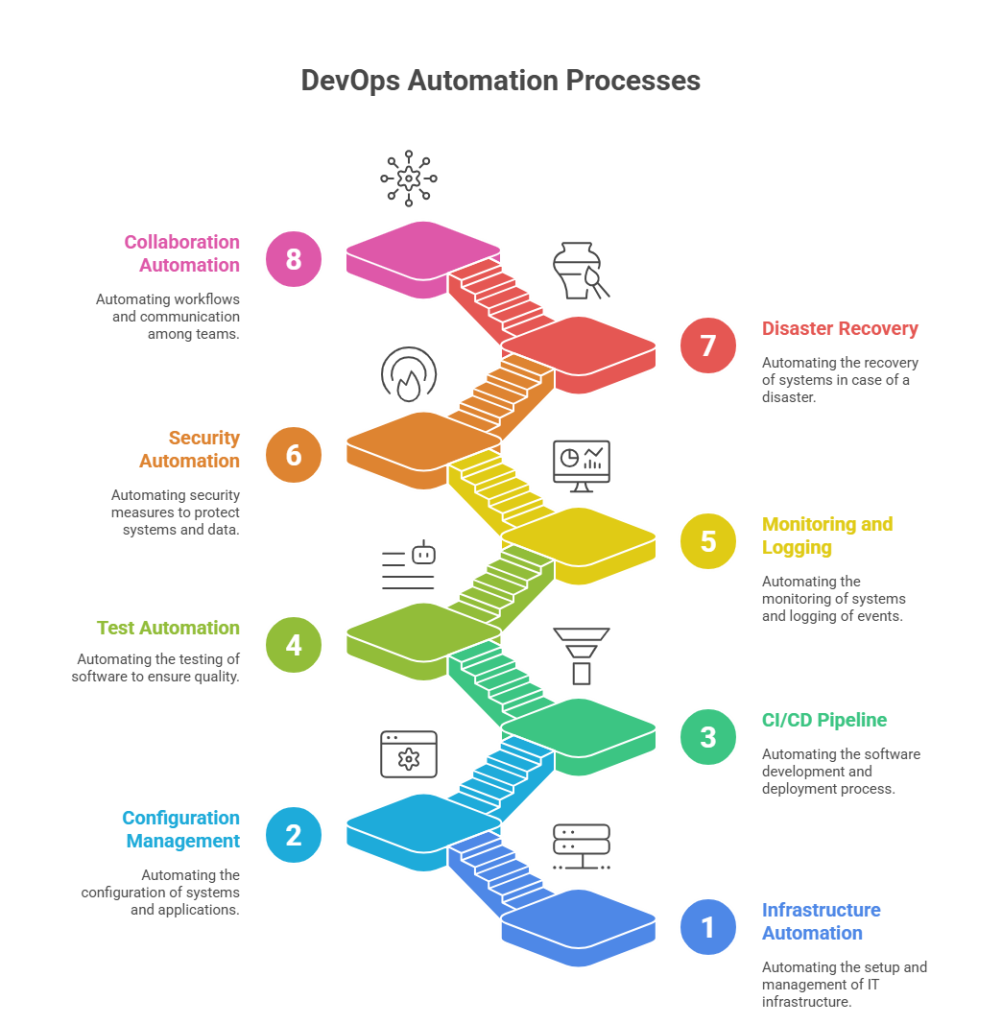
DevOps automation is implemented through a set of well-defined processes that streamline the entire software delivery lifecycle.
These processes ensure consistency, reduce operational risk, and enable teams to manage complex systems efficiently as applications and infrastructure scale, supported by modern scripting and automation practices.
Infrastructure Automation
Infrastructure automation focuses on provisioning and managing servers, networks, and cloud resources through code. Instead of manually setting up environments, teams define infrastructure requirements using reusable templates.
This approach ensures faster environment creation, consistency across stages, and easier scalability in cloud and hybrid setups.
Configuration Management Automation
Configuration management automation keeps systems aligned with defined standards. It ensures that software versions, dependencies, and system settings remain consistent across all environments. By automating configuration updates, teams can prevent drift and reduce production issues caused by mismatched configurations.
CI/CD Pipeline Automation
CI/CD automation enables code changes to move seamlessly from development to production. Builds, tests, and deployments are triggered automatically when new code is committed.
This process helps teams deliver updates frequently while maintaining code quality and deployment reliability.
Test Automation
Automated testing validates code changes early and continuously. Unit, integration, and regression tests run automatically within pipelines, enabling teams to detect defects before they reach production. This reduces rework and supports faster, more confident releases.
Monitoring and Logging Automation
Monitoring and logging automation provides real-time visibility into system performance and application health.
Automated alerts, metric collection, and log analysis help teams quickly identify issues and respond before they impact users, supporting proactive operations.
Security Automation
Security automation integrates security checks directly into development and deployment workflows. Automated vulnerability scans, policy enforcement, and access controls help teams address risks early without slowing down delivery, making security a shared responsibility.
Disaster Recovery Automation
Disaster recovery automation ensures systems can recover quickly from failures. Automated backups, failover mechanisms, and recovery scripts reduce downtime and protect critical data, helping businesses maintain continuity during unexpected events.
Collaboration and Workflow Automation
Collaboration automation connects tools used by development, operations, and business teams. Automated notifications, approvals, and workflow integrations reduce delays and improve coordination, ensuring everyone stays aligned throughout the delivery process.
Best DevOps Automation Tools
Choosing the right tools is critical to implementing reliable, scalable automation workflows. DevOps automation tools help teams standardize processes, reduce manual effort, and manage complex infrastructure and application lifecycles efficiently.
Below are some widely adopted tools that support different aspects of DevOps automation –
Terraform
Terraform is an infrastructure-as-code tool used to provision and manage cloud resources through declarative configurations. It allows teams to define infrastructure in code and apply changes consistently across environments.
Terraform supports multi-cloud setups, making it easier to manage infrastructure at scale while maintaining version control and repeatability.
Jenkins
Jenkins is a popular automation server for building CI/CD pipelines. It automates tasks such as code builds, testing, and deployments, enabling faster and more reliable releases.
With a large plugin ecosystem, Jenkins integrates easily with a wide range of development, testing, and deployment tools used across DevOps workflows.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It helps teams run applications reliably in production by handling container orchestration, load balancing, and self-healing.
Kubernetes is especially valuable for organizations adopting microservices and cloud-native architectures.
Docker
Docker enables applications to be packaged into lightweight, portable containers. Containers ensure that applications run consistently across different environments, reducing issues caused by environmental differences.
Docker plays a key role in DevOps automation by simplifying application delivery and supporting faster deployments.
Ansible
Ansible is a configuration management and automation tool that uses simple, human-readable playbooks. It helps automate system configurations, application deployments, and routine operational tasks.
Ansible’s agentless approach makes it easy to adopt and integrate into existing environments.
DevOps Automation Best Practices
Implementing automation successfully requires more than just tools. Following proven DevOps best practice guidelines helps teams build sustainable, secure, and scalable automation workflows that support long-term growth and continuous improvement.
Adopt CI/CD Pipelines Early
Introducing CI/CD pipelines early in the development lifecycle helps teams establish consistent delivery processes. Early adoption allows automation to evolve alongside the application, reducing rework and improving release confidence over time.
Enable Automated Testing Workflows
Automated testing should be integrated into every stage of the pipeline. Automatically running tests on each code change helps identify defects early, maintain quality standards, and prevent unstable code from reaching production.
You Might Also Like:
Focus on Observability Metrics
Observability goes beyond basic monitoring. Teams should automate the collection of metrics, logs, and traces that provide insights into system behavior. Clear visibility into performance and reliability supports faster issue resolution and informed decision-making.
Reduce Manual Work with Automation
Manual interventions increase the risk of errors and slow down delivery. Automating repetitive operational tasks improves consistency and enables teams to focus on higher-value engineering work rather than routine maintenance.
Integrate Security
Security should be embedded directly into automated pipelines. Automated vulnerability scanning, policy enforcement, and access controls help teams address risks continuously without disrupting delivery speed.
Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as code enables teams to manage environments through version-controlled definitions. This approach ensures consistency, simplifies rollbacks, and supports scalable infrastructure management across cloud environments.
Enable Self-Service Infrastructure
Self-service models allow developers to provision resources through automated workflows without waiting for manual approvals. This reduces bottlenecks while maintaining governance and compliance standards.
Start Your DevOps Automation Journey with BigDataCentric
Building effective automation requires the right mix of strategy, tools, and execution experience. BigDataCentric helps organizations design and implement DevOps Automation workflows that align with their business goals, delivery timelines, and infrastructure maturity.
Instead of applying one-size-fits-all solutions, we focus on creating automation pipelines that align with your existing development and operational processes.
From infrastructure automation and CI/CD pipeline setup to monitoring, security, and configuration management, BigDataCentric supports end-to-end automation initiatives.
Teams working with cloud platforms, containerized applications, or distributed systems can streamline deployments and improve system reliability through well-structured automation frameworks.
This approach complements modern cloud practices already used across scalable DevOps and cloud computing environments.
By combining proven tools, industry-aligned processes, and practical DevOps best practice principles, BigDataCentric enables faster releases, reduced operational risk, and better collaboration across teams.
Whether you are starting with basic automation or optimizing existing pipelines, structured guidance ensures automation delivers measurable outcomes rather than added complexity.
Need Help Building DevOps Automation Pipelines?
Design scalable automation workflows that support continuous delivery and cloud-native systems.
Conclusion
DevOps automation has become a foundational capability for organizations aiming to deliver software faster, more reliably, and at scale. By automating infrastructure, testing, deployments, monitoring, and security, teams can eliminate repetitive manual work and reduce operational risks that slow down delivery.
Automation also strengthens collaboration between development and operations, ensuring consistent workflows across environments.
As systems grow more complex and cloud adoption accelerates, automation enables businesses to maintain stability while responding quickly to change. When implemented with the right tools, processes, and DevOps best practice principles, automation supports continuous improvement and long-term scalability.
Organizations that invest in structured DevOps automation initiatives position themselves to deliver higher-quality software with greater efficiency and confidence.
FAQs
-
How is automation implemented in DevOps?
Automation in DevOps is implemented through CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, automated testing, and monitoring. Tools automate builds, deployments, configurations, and system checks to ensure consistency and speed.
-
What are the 7 C's of DevOps?
The 7 C’s typically include Continuous Development, Continuous Integration, Continuous Testing, Continuous Deployment, Continuous Monitoring, Continuous Feedback, and Continuous Operations. Together, they support an end-to-end automated delivery cycle.
-
Is selenium part of DevOps?
Selenium is not a DevOps tool itself but is widely used within DevOps pipelines for automated testing. It helps validate application functionality during CI/CD workflows.
-
What are the four types of automation systems?
The four main types are fixed automation, programmable automation, flexible automation, and integrated automation. Each type varies in flexibility, scalability, and level of human involvement.
-
Does DevOps replace an SDLC?
DevOps does not replace the SDLC; it enhances it. DevOps integrates continuous practices across SDLC phases to improve speed, collaboration, and delivery quality.

Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
Toggle- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




