Generative AI in Software Testing: Types, Benefits, and Testing Tools

Blog Summary:
This blog explores the impact of Generative AI on Software Testing, including speed, scalability, and quality assurance outcomes. It highlights testing types, operational benefits, and intelligent automation roles across DevOps workflows. The discussion also includes tools and implementation insights for modern testing teams.
Software testing is no longer just about validating features before release. With frequent deployments, complex architectures, and rising user expectations, testing teams are under constant pressure to move faster without compromising quality.
Traditional testing methods struggle to keep up with this pace, especially when applications change frequently, and test coverage must scale continuously.
This is where Generative AI in Software Testing is changing the landscape. Instead of relying solely on predefined scripts and manual effort, testing processes can now learn from application behavior, generate test cases dynamically, and adapt to changes in real time.
These capabilities help teams address recurring challenges, including test maintenance overhead, delayed releases, and missed defects.
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-native systems, DevOps pipelines, and continuous delivery models, the role of intelligent testing becomes even more critical. By combining data-driven insights with automation, modern testing teams can shift from reactive quality checks to proactive quality engineering.
This blog explores how generative approaches are redefining software testing, the types of testing they support, key benefits, tools, and how businesses can implement them effectively.
What is Generative AI in Software Testing?
Generative AI in Software Testing refers to the use of models that can create, adapt, and improve testing artifacts autonomously by learning from data, application behavior, and historical test results.
Instead of relying solely on static test scripts written by testers, generative systems can automatically generate test cases, test data, and even test scenarios as the application evolves.
Unlike traditional automation, which follows predefined rules, generative approaches analyze patterns across code changes, user flows, logs, and past defects. This allows testing systems to simulate real-world usage more effectively and uncover edge cases that might be missed during manual or scripted testing. As a result, teams can achieve broader test coverage without significantly increasing effort.
In software testing, generative techniques play a distinct role by focusing on creation rather than prediction or classification. They help testing frameworks design meaningful tests, suggest assertions, and automatically adapt to UI or workflow changes.
This capability is especially valuable in agile and DevOps environments, where AI in DevOps supports rapid application changes and ensures tests remain reliable across frequent releases.
By embedding these capabilities into the testing lifecycle, organizations can move closer to continuous, intelligent quality assurance. Testing becomes less about maintaining scripts and more about validating business outcomes, performance, and user experience at scale.
Why Software Testing Needs Generative AI Today?
Modern software development moves so quickly that traditional testing approaches often become bottlenecks. Agile sprints, frequent releases, and continuous integration pipelines demand faster feedback cycles, but manual testing and rigid automation struggle to keep pace.
As applications grow more complex, relying solely on scripted tests increases maintenance effort and leaves coverage gaps.
Generative AI in Software Testing addresses these challenges by introducing adaptability into the testing process. Instead of rewriting tests whenever an application changes, intelligent systems can analyze updates to workflows, UI elements, and data patterns and adjust or generate tests accordingly.
This reduces dependency on constant human intervention while keeping test suites relevant across releases.
Another key reason testing needs this shift is the growing diversity of user behaviors and environments. Modern applications operate across devices, platforms, and configurations, making it difficult to manually anticipate every scenario.
AI-powered software testing can model realistic user journeys, identify anomalous patterns, and flag potential risks before they affect end users.
Finally, quality expectations are higher than ever. Defects discovered late in the lifecycle directly impact customer trust and business revenue. By using data-driven insights and learning from historical defects, teams can detect issues earlier and prioritize testing efforts more effectively.
This makes generative approaches not just an innovation, but a practical necessity for maintaining quality in today’s fast-moving development ecosystems.
Types of AI Testing
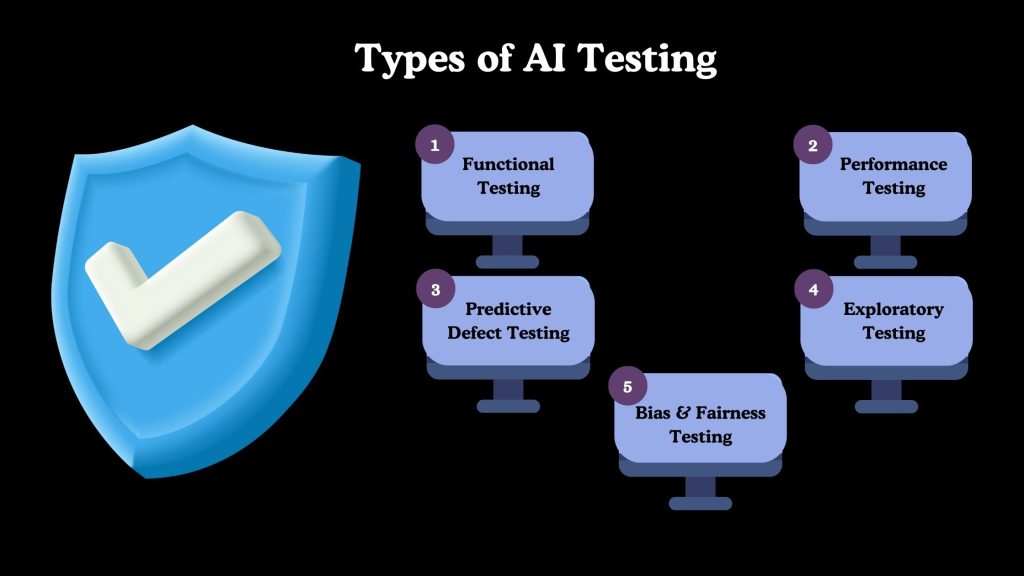
AI-driven testing is not limited to a single testing approach. It supports multiple testing types by adapting to application behavior, data patterns, and user interactions. Each type addresses a specific quality risk, helping teams improve coverage and accuracy across the testing lifecycle.
Functional Testing
In functional testing, AI models analyze application workflows and expected behaviors to automatically generate test cases.
Instead of relying solely on predefined scenarios, AI-driven software testing identifies variations in inputs, edge cases, and business rules that may not be apparent during manual design. This improves functional coverage while reducing the effort required to maintain test scripts as features evolve.
Performance Testing
AI-powered performance testing goes beyond static load scenarios. By learning from past system behavior, it can simulate realistic traffic patterns and predict how applications will perform under varying conditions. Generative models help identify performance bottlenecks early by dynamically adjusting test load based on system responses rather than fixed thresholds.
Predictive Defect Testing
Predictive defect testing focuses on identifying the parts of the application most likely to fail. By analyzing historical defect data, code changes, and usage patterns, artificial intelligence in software testing highlights high-risk modules.
This allows teams to prioritize testing efforts and reduce the chances of critical issues reaching production.
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing traditionally depends on the tester’s intuition and experience. With AI support, systems can explore applications autonomously by mimicking user behavior, navigating unfamiliar paths, and interacting with UI elements dynamically.
This approach uncovers hidden defects that structured test cases might miss, especially in complex or rapidly changing applications.
Bias & Fairness Testing
As applications increasingly rely on data-driven logic, ensuring fairness and unbiased behavior becomes essential. AI-based testing can analyze outputs across datasets and user profiles to detect inconsistencies or unintended bias.
This type of testing is particularly important for systems handling recommendations, personalization, or decision-making logic.
Scale Testing Without Increasing Effort
Enable scalable, resilient automation with Generative AI in Software Testing for complex applications.
Benefits of Generative AI in Software Testing

Generative approaches bring practical improvements to how testing teams plan, execute, and maintain quality processes. These benefits focus on reducing manual effort while improving accuracy, speed, and reliability across the testing lifecycle.
Faster Test Creation
Generative models can analyze application behavior, user flows, and existing test data to automatically create meaningful test cases. This eliminates the need for manual test design for every new feature or change.
Testing teams can achieve broader coverage early in the development cycle. As a result, quality checks begin sooner without slowing down delivery timelines.
Self-Healing Test Automation
Test automation often breaks when UI elements or workflows change slightly. Generative AI in Software Testing enables scripts to detect these changes and automatically update locators or paths.
This reduces false failures caused by minor updates. Teams spend less time fixing tests and more time improving overall quality.
Reduces Time-to-Market
By minimizing manual test creation and maintenance, testing cycles become significantly shorter. Faster feedback allows developers to resolve issues earlier in the pipeline.
This improves release confidence while keeping deployment schedules on track. Businesses can deliver updates faster without compromising stability or performance.
Optimizing Regression Testing
Regression test suites tend to grow over time, increasing execution effort and cost. AI-driven software testing analyzes code changes and historical test results to identify which tests are truly necessary.
It prioritizes high-impact scenarios while removing redundancy. This keeps regression testing efficient and focused with every release.
Enables Real-Time Monitoring
AI-driven testing systems continuously observe application behavior during test execution. They analyze logs, metrics, and responses to identify anomalies in real time. This helps teams catch performance drops or functional issues immediately. Real-time insights reduce the risk of defects progressing unnoticed.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical defect data and testing trends to anticipate future risks. Artificial intelligence in software testing highlights modules that are more likely to fail based on past patterns. This allows teams to allocate testing efforts strategically. Proactive risk identification leads to more stable and reliable releases.
You Might Also Like:
What is the Role of AI in Software Testing?
AI strengthens software testing by making it more adaptive, data-driven, and scalable. Instead of focusing only on executing tests, it supports smarter planning, analysis, and continuous improvement across the testing lifecycle.
Test Automation Enhancement
AI improves test automation by making scripts more resilient to application changes. It analyzes UI updates, workflow changes, and data variations to adjust test execution automatically.
This reduces brittle tests that fail due to minor changes. Automation becomes easier to scale across frequent releases. Teams can rely on stable test results without constant manual intervention.
Defect Prediction and Root Cause Analysis
AI analyzes historical defect data, code commits, and test outcomes to predict where failures are most likely to occur. It helps teams identify high-risk modules before defects appear in production.
When failures occur, AI correlates test results with recent changes to identify root causes faster. This reduces investigation time and improves resolution accuracy. Testing efforts become more focused and efficient.
UI and Visual Testing
UI and visual testing benefit from AI’s ability to recognize patterns and visual differences. AI compares layouts, spacing, colors, and element positions across browsers and devices. It detects subtle visual issues that traditional assertions often miss.
This is especially valuable for responsive and cross-platform applications. Consistent visual quality improves user experience and brand reliability.
NLP-Based Test Automation (Plain English Scripting)
Natural language processing enables testers to write test cases in plain English rather than code. AI interprets these instructions and converts them into executable test scripts. This lowers the technical barrier to creating tests. Business users and QA teams can collaborate more effectively. Test scenarios remain easier to understand and maintain over time.
AI in Performance and Load Testing
AI enhances performance testing by generating load patterns based on real user behavior. It adjusts test conditions dynamically as system performance changes. This helps uncover bottlenecks that static load tests may miss.
AI also analyzes performance trends across test runs. Teams gain more realistic insights into system scalability and stability.
AI in Security Testing
AI supports security testing by continuously monitoring application behavior and traffic patterns. It identifies anomalies that may indicate vulnerabilities or attacks. AI can simulate malicious behavior to test system defenses.
This proactive approach helps detect security risks early. Applications become more resilient against evolving threats.
Continuous Testing in DevOps and CI/CD
AI enables continuous testing by integrating intelligence into DevOps and CI/CD pipelines. It prioritizes tests based on recent code changes and risk impact. This ensures fast feedback without slowing deployments.
AI also helps reduce redundant testing. Continuous quality becomes achievable even with rapid release cycles.
Generative AI vs Manual vs Automated Software Testing
| Aspect | Manual Software Testing | Automated Software Testing | Generative AI in Software Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test Creation | Test cases are written manually based on requirements and the tester’s experience | Scripts are created using predefined frameworks and rules | Tests are generated dynamically by learning from application behavior and data |
| Adaptability to Change | Requires high manual effort when UI or workflows change | Scripts often break with minor changes and need maintenance | Automatically adapts to changes using self-learning and pattern recognition |
| Test Coverage | Limited by human capacity and time constraints | Broader coverage but restricted to scripted scenarios | Expands coverage by discovering edge cases and unseen user paths |
| Maintenance Effort | High effort to update and re-execute tests repeatedly | Moderate to high maintenance due to brittle scripts | Minimal maintenance due to self-healing and adaptive tests |
| Speed of Execution | Slow and dependent on tester availability | Faster execution, but setup and updates take time | Fast execution with continuous optimization and learning |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale across large applications | Scales with infrastructure but requires script upkeep | Scales easily across complex systems with minimal manual input |
| Insight Generation | Relies on tester observations | Limited to pass/fail reports | Provides predictive insights and risk-based recommendations |
| Fit for DevOps & CI/CD | Not suitable for continuous pipelines | Partially suitable with frequent maintenance | Well-suited for continuous testing in DevOps environments |
Popular GenAI Testing Tools
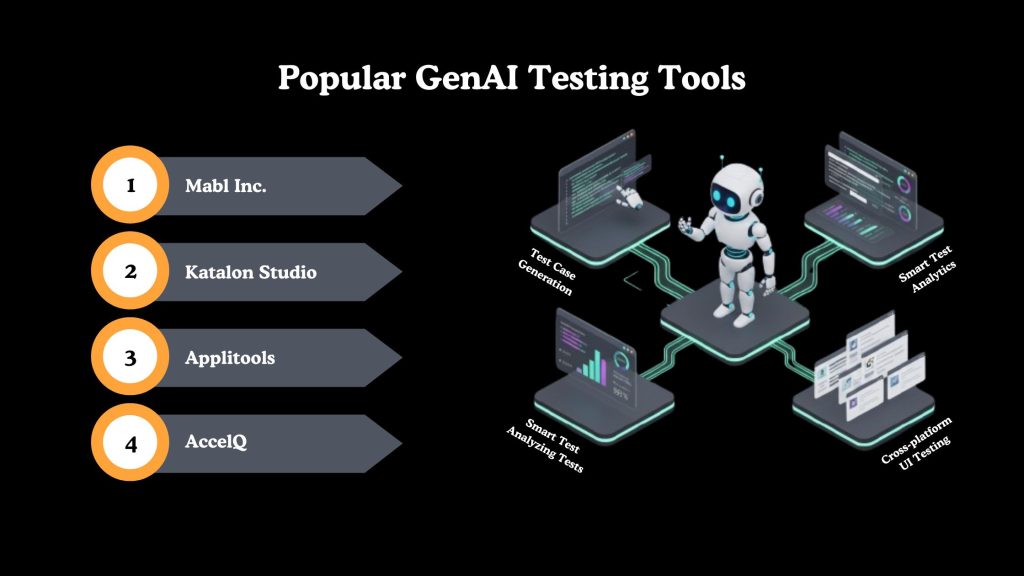
Several modern testing platforms are integrating generative and intelligent capabilities to improve automation, test maintenance, and overall testing efficiency. Below are some widely adopted tools for AI-driven testing.
Mabl Inc.
Mabl is a cloud-based testing platform that uses AI to simplify end-to-end test automation. It automatically creates and maintains tests by learning from application behavior.
The platform reduces flaky tests through self-healing capabilities and provides actionable insights from test results. Mabl fits well into CI/CD pipelines, enabling continuous testing with minimal manual effort.
Katalon Studio
Katalon Studio combines test automation with intelligent features to support web, mobile, API, and desktop testing. It leverages AI to assist in test generation, execution optimization, and failure analysis.
The platform is suitable for teams with mixed technical expertise, offering both scriptless and script-based testing options. Its analytics help teams understand quality trends across releases.
Applitools
Applitools specializes in AI-powered visual testing. It uses advanced visual comparison techniques to detect UI inconsistencies across browsers, devices, and screen sizes.
Instead of relying on pixel-by-pixel checks, Applitools understands visual structure, reducing false positives. This makes it especially valuable for ensuring consistent user experiences in modern applications.
AccelQ
AccelQ is a codeless test automation platform enhanced with AI-driven capabilities. It simplifies test design, execution, and maintenance through natural-language-driven workflows.
AccelQ automatically adapts to application changes, reducing script breakage. It supports continuous testing and integrates easily with DevOps tools.
Why Choose BigDataCentric for Generative AI–Driven Software Testing?
BigDataCentric approaches software testing as a strategic quality function rather than a standalone activity. By combining expertise in data-driven systems, modern testing practices, and intelligent automation, teams help organizations build testing frameworks that scale with evolving applications.
The focus remains on improving reliability, speed, and decision-making across the testing lifecycle.
With experience across data science, analytics-driven platforms, and DevOps-aligned delivery models, BigDataCentric enables the practical adoption of Generative AI in Software Testing.
Testing strategies are designed to integrate smoothly with existing CI/CD pipelines, ensuring continuous validation without disrupting development velocity. This helps organizations reduce testing bottlenecks while maintaining consistent quality standards.
BigDataCentric also emphasizes outcome-driven testing. Instead of focusing solely on execution metrics, testing initiatives are aligned with business goals, including faster releases, fewer production defects, and improved user experience. Intelligent insights from test data support better prioritization and risk assessment across releases.
By aligning advanced testing capabilities with scalable architectures and real-world application demands, BigDataCentric helps organizations move toward intelligent, future-ready quality engineering practices.
Ready to Upgrade Your Testing Strategy?
Use Generative AI in Software Testing to move beyond static scripts and adopt intelligent quality practices.
A Final Word
Software testing is evolving from a support function to a core enabler of reliable, scalable software delivery. As applications grow more complex and release cycles shorten, traditional testing methods alone are no longer sufficient to meet quality expectations. Intelligent approaches bring adaptability, speed, and deeper insights into the testing lifecycle.
Generative AI in Software Testing enables teams to move beyond static scripts and reactive fixes. By learning from data, application behavior, and past outcomes, testing becomes more proactive and resilient.
From faster test creation to predictive insights and continuous validation, this shift helps organizations maintain quality without slowing innovation.
As businesses continue to adopt modern development practices, integrating intelligent testing strategies will be essential for long-term success. Teams that embrace this transformation are better positioned to deliver stable, high-performing applications in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
FAQs
-
Is Generative AI Replacing Test Engineers or Empowering Them?
Generative AI is empowering test engineers rather than replacing them. It automates repetitive tasks, allowing testers to focus on strategy, exploratory testing, and quality decisions.
-
What Are The Key Use Cases Of AI In Software Testing?
Key use cases include automated test generation, self-healing test scripts, defect prediction, visual testing, and continuous testing within CI/CD pipelines.
-
Which automation testing tool is in demand in 2025?
Tools that support intelligent automation and low-code testing are in high demand in 2025. Platforms with AI-driven test maintenance and analytics are especially preferred.
-
Can generative AI handle frequent UI changes?
Yes, generative AI can adapt to frequent UI changes by identifying element patterns and automatically updating test logic. This reduces test failures caused by minor UI updates.
-
Is generative AI suitable for agile and DevOps testing?
Generative AI fits well into agile and DevOps testing environments. It supports continuous testing, faster feedback, and adaptive automation across frequent releases.

Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
Toggle- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




