Quicksight VS Tableau: A Detailed BI Platform Comparison

Blog Summary:
Choosing the right analytics platform is essential for turning data into meaningful insights. This blog compares Quicksight and Tableau across key areas, including features, pricing, scalability, and use cases. It helps businesses understand where each tool fits best based on analytics needs and data environments. The guide also highlights how the right implementation approach can maximize the value of either platform.
Modern businesses rely heavily on data to guide decisions, measure performance, and uncover new opportunities. As data volumes grow and sources diversify, choosing the right business intelligence platform is critical to turning raw data into meaningful insights. This is where tools like Amazon QuickSight and Tableau come into the picture, each offering powerful capabilities for analytics and visualization.
The comparison between Quicksight VS Tableau often arises when organizations evaluate cloud-based analytics platforms that can scale with their needs while supporting both technical and non-technical users.
Although both tools aim to simplify data analysis and reporting, they differ significantly in architecture, pricing models, integration capabilities, and advanced analytics features.
This blog offers a structured, practical comparison to help you understand how these platforms perform across key areas, including data integration, visualization, machine learning support, collaboration, and cost.
By the end, you’ll have a clear view of which solution best aligns with your business goals, technical ecosystem, and long-term analytics strategy.
Overview of Quicksight
Amazon QuickSight is a cloud-native business intelligence and analytics service built to help organizations analyze data at scale without managing complex infrastructure.
Designed as a fully managed solution within the AWS ecosystem, it enables teams to create interactive dashboards, perform ad hoc analysis, and securely share insights across the organization.
QuickSight is primarily focused on speed, scalability, and cost efficiency. It uses a serverless architecture and an in-memory calculation engine (SPICE) to deliver fast query performance even on large datasets.
Users can connect to a wide range of data sources, including AWS services and external databases, and visualize information through intuitive charts, tables, and KPIs.
The platform is well-suited for organizations already invested in AWS, as it integrates seamlessly with cloud data warehouses, data lakes, and security services. With built-in machine learning-powered insights and embedded analytics capabilities, QuickSight supports both internal analytics teams and product teams looking to deliver data-driven features to end users.
Major Benefits of Amazon QuickSight

Amazon QuickSight offers capabilities designed for organizations seeking scalable analytics without the overhead of managing infrastructure.
Its cloud-first design, combined with built-in intelligence and flexible access options, makes it suitable for both internal reporting and customer-facing analytics.
Cost-Effective
One of QuickSight’s strongest advantages is its pricing structure. Instead of traditional per-user licensing, it offers a session-based model that allows businesses to pay only when dashboards are accessed.
This makes it especially attractive for organizations with a large number of occasional users, helping control analytics costs as usage scales.
AI-Powered Insights
QuickSight includes machine learning-driven features that automatically surface trends, anomalies, and outliers in data.
These insights help users move beyond static reporting and quickly understand what is happening in their datasets, even without advanced analytics expertise.
Embedded Analytics
The platform is designed to embed dashboards and visualizations directly into applications, portals, or SaaS products. This allows businesses to deliver analytics within their existing software experiences, enabling end users to interact with data without switching tools.
Unified Data Access
QuickSight supports access to multiple data sources through a centralized interface. Whether data resides in cloud storage, data warehouses, or external databases, users can analyze it without complex data movement, maintaining consistency across reports and dashboards.
Deep AWS Integration
Built natively for the AWS ecosystem, QuickSight integrates seamlessly with services such as data lakes, cloud databases, and identity management tools. This tight integration simplifies security, governance, and scalability for teams already operating within AWS.
Adopt Amazon QuickSight with Confidence
Get expert support to implement QuickSight for scalable dashboards and cloud-based analytics.
Overview of Tableau
Tableau is a widely adopted data analytics and visualization platform known for its rich visual capabilities and interactive dashboards.
It enables users to explore data intuitively, uncover patterns, and communicate insights through visually compelling, easy-to-understand reports that are accessible across teams.
Tableau supports a broad range of deployment options, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. This flexibility allows organizations to choose how and where their data is analyzed, making it suitable for enterprises with complex infrastructure requirements.
Users can connect Tableau to various databases, cloud platforms, and files to perform both exploratory and operational analytics.
The platform is especially popular among analysts and data professionals due to its drag-and-drop interface and powerful calculation engine.
With strong support for advanced analytics, collaboration, and enterprise-grade governance, Tableau is often chosen by organizations that prioritize deep data exploration and highly customized visual storytelling.
Major Benefits of Tableau
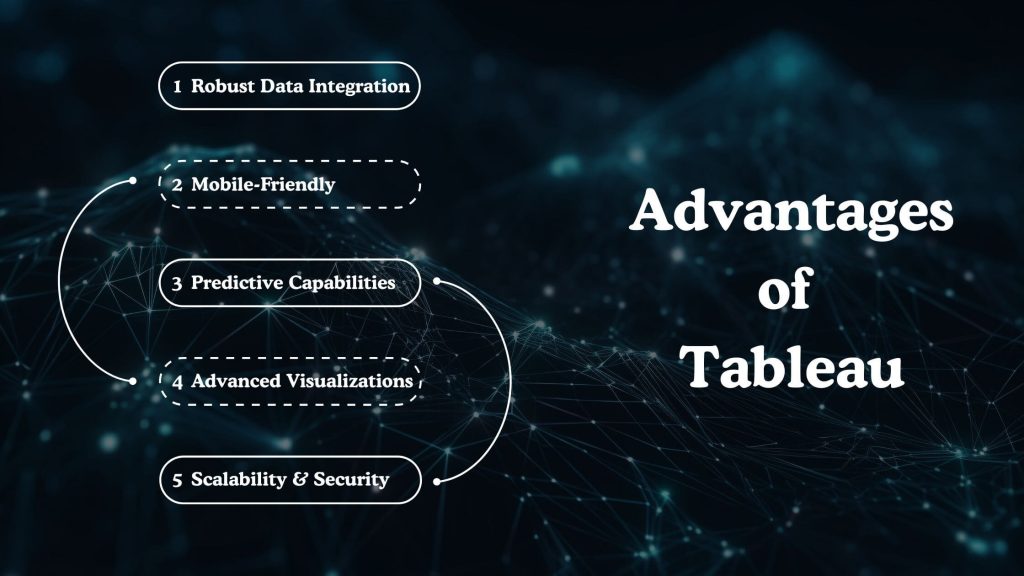
Tableau offers a robust feature set that appeals to organizations seeking advanced data exploration and visually rich analytics. Its flexibility, depth of functionality, and strong user experience make it a preferred choice for data-driven teams across industries.
Powerful Data Integration
Tableau connects seamlessly with a wide variety of data sources, including cloud platforms, on-premises databases, spreadsheets, and big data systems. This extensive connectivity enables organizations to integrate data from multiple sources and perform comprehensive analysis without extensive preprocessing.
Mobile-Friendly & Collaborative
The platform is designed to support analytics on the go, with dashboards optimized for mobile devices. Tableau also enables collaboration through shared dashboards, comments, and subscriptions, keeping teams aligned and enabling decisions based on the same set of insights.
AI & Predictive Capabilities
Tableau includes built-in capabilities for predictive analysis and natural language queries, helping users ask questions of their data in plain language. These features make advanced analytics more accessible and enable deeper insights without requiring complex modeling expertise.
Advanced Visualizations
One of Tableau’s strongest advantages is its ability to create highly interactive and customizable visualizations. Users can design complex charts, maps, and dashboards that adapt dynamically to user interactions, making it easier to uncover trends and tell compelling data stories.
Scalability & Security
Tableau is built to support enterprise-scale deployments, offering role-based access control, data governance, and compliance features. It scales effectively as data volumes and user counts grow, ensuring consistent performance and secure access across the organization.
Quicksight VS Tableau: A Quick Tabular Comparison
| Comparison Factor | Amazon QuickSight | Tableau |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Cloud-native analytics designed for scalable, cost-efficient reporting within cloud ecosystems | Advanced data visualization and deep exploratory analytics |
| Deployment Model | Fully managed, serverless cloud service | Cloud, on-premises, and hybrid deployment options |
| Advanced Analytics | Built-in ML-driven insights for anomaly detection and trend analysis | Strong support for advanced calculations, forecasting, and predictive analysis |
| Pricing Model | Usage-based and session-based pricing, suitable for large viewer audiences | Per-user licensing is typically higher for enterprise-scale usage |
| Data Source Integration | Strong integration with cloud data services and popular databases | Extensive connectivity across cloud, on-prem, and third-party data sources |
| Data Visualization | Clean, functional dashboards focused on performance and clarity | Highly interactive, customizable, and visually rich dashboards |
| Ease of Use | Simple interface aimed at quick adoption for business users | Drag-and-drop interface with a learning curve for advanced features |
| Scalability | Automatically scales without infrastructure management | Scales well but may require planning for large deployments |
Need Clarity on BI Platform Selection?
Our experts evaluate features, costs, and scalability to guide your decision.
Detailed Comparison: Quicksight VS Tableau
When evaluating Quicksight VS Tableau, it’s important to look beyond surface-level features and understand how each platform performs in real-world analytics scenarios.
This detailed comparison breaks down the tools across core functional areas that directly impact usability, performance, and long-term value.
Data Integration and Connectivity
QuickSight is designed with a strong emphasis on cloud-based data connectivity, particularly within AWS environments. It works efficiently with cloud data warehouses, data lakes, and managed databases, allowing teams to analyze data without extensive data movement or duplication. This makes it suitable for organizations operating primarily in cloud-first setups.
Tableau, on the other hand, stands out for its broad data connectivity. It supports a wide range of cloud and on-premises data sources, making it a strong option for businesses with hybrid or legacy data environments. Its ability to blend data from multiple sources gives analysts greater flexibility during exploration.
Data Visualisation and Reporting
QuickSight focuses on delivering clean, performance-oriented dashboards that load quickly and scale well. Its visual components are practical and designed for business reporting, making it easier to share consistent insights across large user bases.
Tableau excels in visual storytelling. It offers extensive customization options, interactive dashboards, and advanced charting capabilities. This makes it ideal for teams that rely on exploratory analysis and need to present complex insights in a visually compelling manner.
Machine Learning Integration
QuickSight includes built-in machine learning features that automatically surface insights, including anomalies, trends, and forecasts. These capabilities reduce the effort required to perform advanced analysis and help business users gain insights without deep technical expertise.
Tableau supports advanced analytics through calculated fields, forecasting models, and integration with external machine learning tools. While it may require more manual setup, it provides greater control for analysts who need customized predictive analysis.
Collaboration and Sharing
QuickSight enables easy sharing of dashboards across large audiences using secure access controls. Its session-based access model works well for organizations that need to distribute insights widely without assigning licenses to every viewer.
Tableau offers mature collaboration features, including shared dashboards, comments, alerts, and subscriptions. These capabilities support ongoing collaboration between analysts and business stakeholders, especially in data-driven teams.
Ease of Use
QuickSight is designed for quick adoption, particularly by business users who need fast access to insights without complex configurations. Its simplified interface helps reduce the learning curve for standard reporting needs.
Tableau provides a powerful drag-and-drop experience but may require more time to master, especially for advanced calculations and custom visualizations. It is better suited for users who regularly perform in-depth data analysis.
Use Cases
QuickSight is commonly used for operational reporting, embedded analytics, and large-scale dashboard distribution, especially in cloud-native environments. It works well for organizations prioritizing scalability and cost efficiency.
Tableau is often chosen for advanced analytics, exploratory data analysis, and executive reporting, where visual depth and flexibility are critical. It fits organizations that value deep data exploration across diverse data sources.
Pricing Model
QuickSight uses a usage-based pricing model, allowing organizations to pay for dashboard usage. This model can significantly reduce costs for businesses with many occasional users.
Tableau uses a per-user licensing model, which can become costly as the number of users grows. However, it offers strong value for teams that rely heavily on advanced analytics and visualization capabilities.
Quicksight VS Tableau – Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between Quicksight VS Tableau largely depends on your organization’s data environment, analytics goals, and budget expectations. Both platforms are capable, but they serve slightly different priorities and user needs.
QuickSight is often the better fit for organizations that operate primarily in cloud environments and need a scalable analytics solution for large user bases.
Its usage-based pricing, serverless architecture, and built-in intelligence make it suitable for companies that want to distribute dashboards widely, embed analytics into applications, or keep operational costs predictable as usage grows.
Tableau is better suited for teams that rely heavily on in-depth data exploration and advanced visual analysis.
If your organization has analysts who need full control over calculations, visual design, and exploratory workflows across diverse data sources, Tableau provides greater flexibility. It is particularly effective for executive reporting, analytical storytelling, and environments where data discovery is a core activity.
From a decision-making perspective, organizations focused on cloud-native analytics and cost efficiency may lean toward QuickSight. At the same time, those prioritizing visual depth, analytical freedom, and mature collaboration features may find Tableau more aligned with their needs.
Still deciding between Quicksight and Tableau?
Get expert guidance to choose the right analytics platform aligned with your business strategy.
A Final Word
The comparison of Quicksight VS Tableau highlights that there is no one-size-fits-all analytics solution. Each platform brings its own strengths, whether it is cloud-native scalability and cost efficiency or advanced visual analytics and deep data exploration.
The right choice ultimately depends on your data landscape, user base, and how insights are consumed across your organization.
This is where BigDataCentric can play a meaningful role in your analytics journey. With expertise in data engineering, business intelligence, and cloud-based analytics solutions, BigDataCentric helps organizations assess their reporting needs, select the right BI platform and BI tools, and implement them effectively.
From data integration and dashboard design to performance optimization and governance, the team ensures that your analytics stack delivers real business value.
Whether you are evaluating Amazon QuickSight for large-scale dashboard distribution or Tableau for advanced analytics and visualization, having the right implementation partner can make a significant difference. With a structured approach and deep domain knowledge, BigDataCentric helps businesses turn analytics investments into actionable, decision-ready insights.
FAQs
-
Is Tableau or QuickSight Easier To Use?
Amazon QuickSight is generally easier for business users who want quick dashboards with minimal setup, especially in AWS environments. Tableau offers more flexibility but has a steeper learning curve for advanced analysis.
-
What is the best alternative to Tableau?
There is no single “best” alternative, as it depends on use cases. Tools like Amazon QuickSight, Power BI, and Looker are commonly chosen based on cloud setup, pricing, and analytics depth requirements.
-
Are people moving away from AWS?
Businesses are not broadly leaving AWS, but some are reassessing their cloud strategies due to unpredictable costs, compliance requirements, and control needs. Instead of a full exit, many organizations are adopting hybrid or on-premises models for stable workloads while continuing to use AWS for scalable and dynamic use cases.
-
Is Tableau becoming obsolete?
Tableau is not becoming obsolete. It remains widely used for advanced analytics, data exploration, and enterprise reporting, especially in organizations that prioritize rich visualizations and deep analytical control.
-
Does QuickSight require coding?
QuickSight does not require coding for standard dashboards and reports. Most analytics can be built using its visual interface, while optional calculations or advanced use cases may involve basic expressions.

Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
Toggle- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




