Why Business Intelligence Projects Fail: 11 Causes and Fixes

Blog Summary:
Want to know why business intelligence projects fail even after heavy investment? This blog explains the 11 major reasons behind BI failure, from poor data quality to low user adoption. It also covers practical steps to fix struggling BI initiatives and best practices to ensure long-term BI success.
Business intelligence has become a critical investment for companies seeking to make smarter decisions with real-time data. From dashboards and reports to predictive analytics, BI solutions are expected to improve efficiency, performance tracking, and strategic planning. However, many organizations still struggle to achieve the outcomes they initially planned.
Despite investing heavily in BI tools, data pipelines, and reporting infrastructure, businesses often face delays, inaccurate insights, low adoption, and inconsistent reporting. In many cases, stakeholders eventually stop trusting the dashboards altogether, and the BI project fails to deliver measurable value.
Understanding Why Business Intelligence Projects Fail is important because failure is rarely caused by one single issue. It usually results from a combination of poor planning, weak data foundations, misalignment, and limited user involvement.
In this blog, we will explore the major reasons behind BI project failures, practical ways to fix them, and best practices to ensure long-term BI success.
Why Business Intelligence Projects Fail Even After Heavy Investment?
Many organizations assume that investing in premium BI tools, hiring analysts, and building dashboards automatically leads to better decision-making. But the reality is different.
Even after spending significant time and money, BI projects can still collapse because the investment is often made in technology rather than in strategy, data readiness, and user adoption.
In most cases, businesses focus on implementing a BI platform quickly without clearly defining what success looks like. Dashboards are created, reports are generated, and data sources are connected—but the insights may not match business priorities. This leads to confusion among teams, a lack of trust in reports, and eventually low usage.
Another common reason is that BI requires continuous improvement. Data changes, business goals evolve, and user needs shift. If a BI system is treated as a one-time project instead of an ongoing process, it quickly becomes outdated. This is one of the biggest reasons why business intelligence projects fail even after heavy investment.
11 Major Reasons Why Business Intelligence Projects Fail

Business intelligence projects often fail not because the technology is weak, but because the foundation and execution strategy are poorly planned. Many organizations invest in BI tools expecting quick results but ignore key factors such as data readiness, stakeholder alignment, and user adoption.
To understand why business intelligence projects fail, it is important to evaluate the root causes that impact reporting accuracy, dashboard usability, and decision-making reliability. Below are the 11 major reasons behind BI project failure.
Unclear Business Goals and Vision
Many BI projects begin without defining what success actually looks like. Teams start building dashboards and reports without knowing which KPIs matter most or what decisions the BI system is expected to support. This results in reports that look visually appealing but do not solve real business problems.
When business goals are unclear, different departments demand different outcomes, and the BI project loses direction. Over time, the solution becomes a data display system rather than a decision-making tool. This confusion becomes one of the biggest reasons why business intelligence projects fail in the early stages.
Lack of Executive Support
BI projects require strong leadership support because they often involve cross-functional collaboration and major changes in reporting processes. Without executive sponsorship, teams may not prioritize the BI initiative, which leads to delays and incomplete implementation.
Executives also play an important role in driving adoption. If leadership does not actively promote BI use, teams continue to rely on spreadsheets and manual reporting. In many cases, BI becomes a “side project,” which directly impacts its success and long-term scalability.
Poor Data Quality Issues
BI insights are only as reliable as the data behind them. If your organization has duplicate entries, missing fields, inconsistent formatting, or outdated data sources, your dashboards will deliver inaccurate results. This creates confusion instead of clarity.
Poor data quality also reduces trust in BI systems. When stakeholders encounter mismatched reports or incorrect numbers, they stop trusting the dashboards and revert to manual methods. Over time, this becomes a critical factor in project failures despite heavy investment.
Struggling with Poor Data Quality in Your BI System?
Fix inconsistent data, eliminate reporting errors, and build reliable dashboards with a structured data quality and governance approach.
No Single Source of Truth
A BI project fails quickly when different teams rely on different datasets, definitions, and reporting standards. For example, sales may calculate revenue differently from finance, and marketing may use different customer segmentation criteria. This creates conflicting reports and confusion in decision-making.
Without a centralized “single source of truth,” BI becomes a debate platform rather than a strategy tool. Instead of using dashboards to take action, teams spend time validating which report is correct. This reduces BI reliability and impacts business confidence.
Weak Data Governance Framework
Data governance ensures that data is properly managed, secure, consistent, and accessible. Without governance, organizations face issues such as unclear data ownership, insufficient data definitions, and inconsistent reporting standards. This leads to errors across dashboards and reports.
Weak governance also makes BI difficult to scale. As the business grows, data sources increase and reporting complexity rises. Without proper governance rules, BI becomes messy, unstructured, and unreliable—making it a major reason for project failures in the long run.
Wrong BI Tool Selection
Many companies choose BI tools based on popularity rather than real requirements. A tool may look powerful, but it might not integrate well with existing databases, cloud platforms, or enterprise BI applications. This creates implementation challenges and slows down project delivery.
Wrong tool selection also impacts scalability and user adoption. If the tool is too complex for business users or lacks required features, teams struggle to use it efficiently. Eventually, the tool becomes underutilized, leading to wasted investment and poor BI outcomes.
Poor Requirement Gathering Process
Requirement gathering is the foundation of a successful BI project, yet many businesses rush this phase. They collect requirements only from IT teams or a limited group of stakeholders. As a result, dashboards are built based on assumptions rather than actual business needs.
When end users are not involved, the BI solution often misses critical KPIs, filters, or reporting formats. This leads to frequent revisions and dissatisfaction. Poor requirement gathering is one of the most common reasons BI solutions fail to deliver value.
Lack of Skilled BI Team
BI projects require a mix of technical and analytical expertise, including data engineers, BI developers, analysts, and domain experts. If the team lacks experience in data modeling, ETL processes, or visualization best practices, the final BI system becomes slow and poorly structured.
A lack of skilled talent also affects troubleshooting and improvement. Teams may struggle with query optimization, dashboard performance, or report accuracy. This leads to delayed deliveries, repeated errors, and system instability, which increases failure risk.
Low User Adoption Rate
Even a well-designed BI solution fails if users do not adopt it. Low adoption happens when dashboards are confusing, difficult to access, or do not provide meaningful insights. If users feel BI does not support their daily work, they avoid using it.
Training and change management are equally important. Many BI implementations skip user onboarding and expect employees to adapt automatically. Without guidance, teams continue using spreadsheets, and BI adoption remains low, which becomes a major reason why projects fail.
Too Many Unused Dashboards
Organizations often create dashboards for every department and KPI without evaluating their actual usefulness. Over time, the BI system becomes overloaded with reports that no one uses. This creates confusion and makes it harder for users to find the right insights.
Unused dashboards also increase maintenance workload. BI teams spend time updating reports that have no impact, while important dashboards remain outdated. This reduces BI efficiency and devalues the system, leading to poor decision-making outcomes.
No Continuous BI Improvement
BI is not a one-time implementation—it needs continuous monitoring and enhancement. Many companies launch BI dashboards and assume the work is done. However, business goals evolve, KPIs change, and data sources expand over time.
If BI systems are not updated regularly, dashboards become outdated and irrelevant. This leads to reduced usage and declining trust among stakeholders. Lack of continuous improvement is a long-term reason why BI projects fail, especially in fast-growing industries.
You Might Also Like:
What Factors Impact Business Intelligence Cost for Your Organization?
How to Fix a Failing Business Intelligence Project?
When a BI project starts to fail, the biggest mistake organizations make is to keep the same approach and hope things will improve.
BI failures are usually not caused by a single technical issue. They happen due to misalignment between business goals, data quality gaps, poor governance, and weak collaboration between teams.
The good news is that most BI projects can be fixed if the organization takes corrective steps early. Below are the most effective ways to recover a failing BI initiative and rebuild it into a reliable decision-making system.
Re-Align with Business Strategy
The first step is to reconnect the BI project with business objectives. Many BI implementations fail because dashboards are built without understanding what the business actually needs.
To fix this, stakeholders must clearly define goals such as improving operational efficiency, tracking revenue performance, or monitoring customer behavior.
Once goals are defined, the BI team should rebuild KPIs and reporting structures around those priorities.
This alignment ensures dashboards are not just reporting numbers but delivering insights that support strategic decision-making. It also helps clarify which data matter most and which reports should be prioritized.
Establish Data Governance
A failing BI project often suffers from inconsistent definitions, poor access control, and unclear data ownership. Establishing a strong data governance framework is essential to ensure that data is standardized, validated, and managed properly across departments.
Governance should include rules for data definitions, reporting standards, security policies, and ownership responsibilities. When governance is in place, teams trust the BI system more because reports become consistent and reliable. Strong governance also reduces confusion caused by multiple versions of the same KPI.
Prioritize Data Quality
Data quality issues are one of the biggest reasons BI dashboards lose credibility. To fix this, organizations must start by identifying data errors such as missing records, duplicate entries, inconsistent formats, and outdated values.
These issues should be corrected at the source level rather than just being cleaned up at the reporting stage.
Once cleaning is done, businesses should implement automated validation checks and monitoring systems. This ensures that the BI platform continuously receives accurate data. When data becomes reliable, user trust improves, and BI adoption increases significantly.
Implement Agile Development
Many BI projects fail because they follow a rigid approach that delivers dashboards after long development cycles. By the time reports are ready, business needs may already have changed. Agile development solves this by delivering BI features in small, measurable phases.
With agile BI implementation, teams can collect feedback early, make quick improvements, and reduce the risk of building unused dashboards. Regular sprint reviews also help stakeholders stay involved, ensuring the BI system remains aligned with real user expectations.
Bridge the Technical-Business Gap
A major reason BI projects struggle is the communication gap between technical teams and business users. Technical teams focus on data models and architecture, while business users focus on usability and decision-making.
If both sides are not aligned, dashboards may be technically correct but practically useless.
To fix this, organizations should encourage frequent collaboration through workshops, feedback sessions, and reporting reviews. Having business analysts or BI consultants act as a bridge between both teams also improves clarity.
When communication improves, BI becomes more meaningful, accurate, and user-friendly.
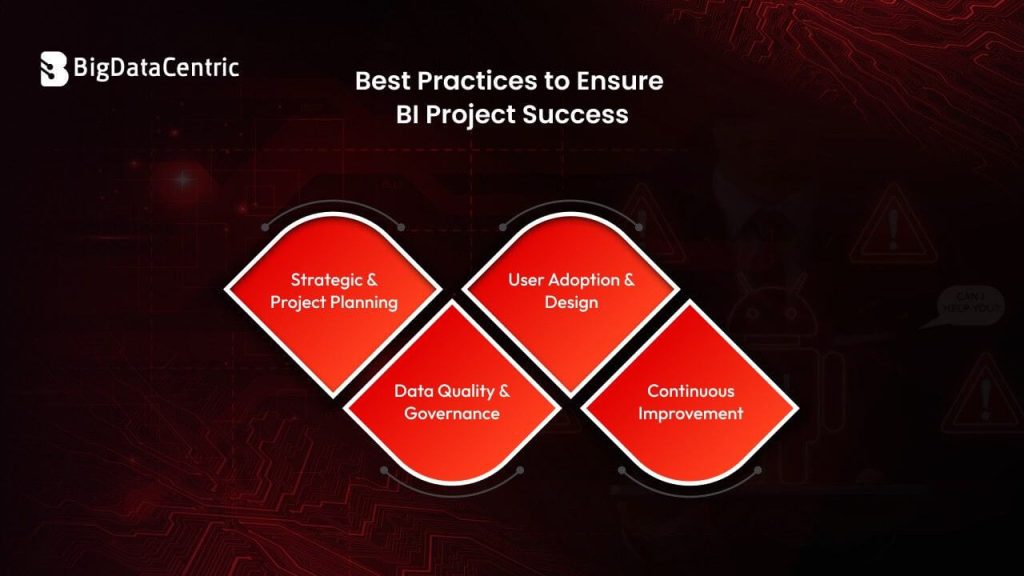
Best Practices to Ensure Business Intelligence Project Success
To avoid BI failures, businesses need to treat BI as a long-term strategy rather than a one-time implementation. Successful BI projects focus on planning, data reliability, user adoption, and continuous improvement to ensure dashboards remain useful and trusted.
Below are best practices to reduce the risk of BI failure and improve long-term success.
Strategic & Project Planning
A successful BI project starts with clear planning, defined KPIs, and well-documented business requirements. When teams know what decisions the BI system should support, the implementation becomes more focused and outcome-driven.
It is also important to create a realistic roadmap with timelines, responsibilities, and measurable goals. Strong planning ensures the BI project stays aligned with business priorities and avoids unnecessary dashboard development.
Data Quality & Governance
Data accuracy is the foundation of BI success, so organizations must focus on maintaining clean, consistent, and validated data sources. Implementing automated checks and regular audits ensures BI dashboards deliver reliable insights.
Along with quality, governance is equally important for maintaining standardized data definitions and proper access controls. Strong governance prevents confusion, reduces reporting conflicts, and increases trust in BI systems.
User Adoption & Design
Even the best BI system fails if users do not use it. BI dashboards should be designed with the end user in mind, focusing on clarity, usability, and relevant KPIs that support daily decision-making.
User training and change management should also be part of the BI rollout. When users understand how to use BI dashboards effectively, adoption improves and the overall value of BI increases.
Continuous Improvement
BI success depends on continuous evaluation and refinement. Business goals evolve over time, and dashboards must be updated to reflect new KPIs, market changes, and operational priorities.
Regular feedback sessions, dashboard performance monitoring, and KPI reviews ensure the BI system stays relevant. Continuous improvement prevents BI stagnation and helps maintain long-term business impact.
How BigDataCentric Helps Businesses Build Successful BI Solutions?
BigDataCentric helps businesses build BI solutions that are not only visually appealing but also reliable, scalable, and aligned with real business objectives.
We start by understanding your business goals, reporting needs, and key decision-making areas to ensure the BI strategy is clear from the beginning. This approach helps avoid confusion, unnecessary dashboards, and reporting gaps.
Our team focuses on building strong data foundations by improving data quality, integrating multiple data sources, and creating a structured single source of truth. We also support business intelligence automation to streamline reporting and improve efficiency.
We also implement data governance practices to ensure consistency, security, and standardized KPI definitions across departments. This makes reporting more accurate and improves trust in dashboards.
In addition, we help organizations improve BI adoption by designing user-friendly dashboards and delivering role-based reporting experiences. We also support continuous BI improvement through regular performance monitoring, KPI reviews, and dashboard enhancements.
With BigDataCentric, businesses can reduce BI implementation risks and build BI systems that deliver long-term value and measurable results.
Need Help Fixing a Failing BI System?
Re-align your BI strategy, eliminate reporting gaps, and build dashboards that deliver actionable insights and measurable ROI.
Conclusion
Business intelligence projects often fail due to unclear goals, poor data quality, weak governance, low adoption, and lack of continuous improvement. Understanding why business intelligence projects fail helps organizations avoid common mistakes and build BI systems that deliver real decision-making value.
The key to BI success lies in aligning BI with business strategy, strengthening data governance, ensuring clean data, and focusing on user-friendly reporting. With the right planning and continuous optimization, BI can become a powerful asset that improves performance, efficiency, and business growth.
FAQs
-
Why do BI dashboards fail to drive decisions?
BI dashboards fail when they show too much data but lack actionable insights. Poor data quality, unclear KPIs, and irrelevant reporting also reduce trust, so teams stop using dashboards for decisions.
-
What causes KPI confusion in BI dashboards?
KPI confusion happens when different teams use different definitions for the same metric. Lack of data governance and no single source of truth often leads to inconsistent reporting across dashboards.
-
When should a company rebuild its BI system?
A company should rebuild its BI system when dashboards are outdated, reports are inconsistent, and users no longer trust the data. Frequent manual reporting and poor scalability are also strong signs for rebuilding.
-
What are the biggest challenges in BI data integration?
The biggest challenges include integrating multiple data sources, inconsistent data formats, missing values, and duplicate records. Real-time syncing and maintaining data accuracy across systems are also major issues.
-
What is the role of ETL pipelines in BI success?
ETL pipelines collect, clean, transform, and load data into BI systems for reporting. Strong ETL processes ensure data consistency, accuracy, and timely updates, which directly improves dashboard reliability.

Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
Toggle- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




