Get in Touch With Us
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.
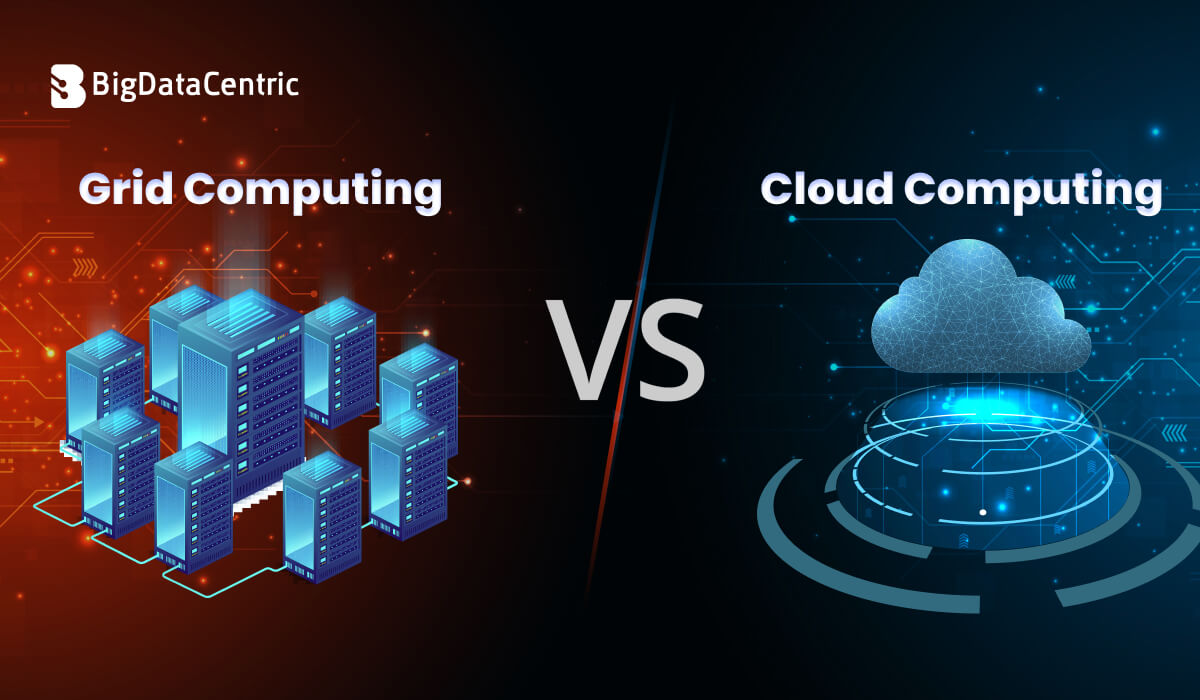
As organizations process larger datasets and run increasingly complex applications, distributed computing models have become essential. Two commonly compared paradigms are grid computing vs cloud computing. While both involve distributed resources, their architecture, scalability, and use cases differ significantly.
Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right approach for performance, cost, and flexibility.
What is Grid Computing?
Grid computing is a distributed computing model where multiple independent computers work together to solve a single large problem. These systems are often geographically distributed and coordinated through middleware.
Key Characteristics of Grid Computing
- Uses heterogeneous resources
- Resources belong to different administrative domains
- Designed for batch processing and scientific workloads
- Limited elasticity
Grid computing gained popularity in research institutions and academia.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing delivers computing resources—such as servers, storage, and applications—over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. Resources are virtualized and centrally managed by cloud providers.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand resource provisioning
- High scalability and elasticity
- Centralized management
- Supports IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS models
Cloud computing is widely used in enterprise and consumer applications.
Grid Computing vs Cloud Computing: Core Differences
| Aspect | Grid Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Ownership | Distributed, multiple owners | Centralized provider |
| Scalability | Limited, manual | Elastic and automatic |
| Cost Model | Fixed infrastructure | Pay-as-you-go |
| Virtualization | Rare | Core component |
| Use Cases | Scientific research, simulations | Web apps, AI, DevOps |
| Management | Complex middleware | Managed services |
Architecture Comparison
Grid Computing Architecture
- Independent nodes connected via networks
- Middleware for job scheduling
- No centralized control plane
Cloud Computing Architecture
- Centralized data centers
- Virtual machines and containers
- Managed orchestration layers
Cloud computing abstracts infrastructure complexity, while grid computing exposes it.
Python Example: Distributed Task in Grid Computing Style
Below is a simplified Python example simulating a grid-style workload using multiprocessing.
from multiprocessing import Pool
def compute_square(x):
return x * x
if __name__ == "__main__":
with Pool(4) as pool:
results = pool.map(compute_square, range(10))
print(results)
This model distributes tasks across worker processes, similar to grid workloads.
Python Example: Cloud-Style Scalable Processing
In cloud environments, scalable frameworks are commonly used.
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def process_data(x):
return x ** 2
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) as executor:
results = list(executor.map(process_data, range(10)))
print(results)This approach scales dynamically and integrates well with cloud-native services.
Use Cases: Grid Computing vs Cloud Computing
Grid Computing Use Cases
- Climate modeling
- Genomic research
- Particle physics simulations
- Academic research projects
Cloud Computing Use Cases
- Web and mobile applications
- Machine learning pipelines
- DevOps automation
- Big data analytics
- SaaS platforms
Cost and Resource Management
Grid computing often requires upfront infrastructure investment and ongoing maintenance. Resource allocation is static, leading to underutilization.
Cloud computing offers:
- Usage-based pricing
- Automatic scaling
- Reduced operational overhead
This makes cloud computing more attractive for businesses with variable workloads.
Security and Governance
Grid environments rely on federated security models, which can be complex to manage.
Cloud platforms provide:
- Centralized identity and access management
- Built-in compliance certifications
- Automated patching and monitoring
Also Read:
When to Choose Grid Computing vs Cloud Computing?
Choose grid computing if:
- You run long-running scientific computations
- Resources are owned by multiple organizations
- Cost constraints prevent cloud adoption
Choose cloud computing if:
- You need elasticity and speed
- Workloads are unpredictable
- You want managed services and automation
Choose the Right Computing Model
We help businesses evaluate grid and cloud computing for modern workloads.
Conclusion
When comparing grid computing vs cloud computing, the key difference lies in ownership, scalability, and management. Grid computing excels in collaborative scientific environments, while cloud computing dominates modern enterprise and digital workloads.
For most organizations today, cloud computing provides greater flexibility, lower operational overhead, and faster innovation—making it the preferred choice for scalable and future-ready systems.