Get in Touch With Us
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.
As global businesses expand, supporting customers in multiple languages has become essential. Traditional chatbots struggle here because they are usually trained in a single language. A Multilingual Chatbot solves that by understanding, processing, and generating text in many languages—often in real time.
This guide explains what multilingual chatbots are, how they work, and how to build one using NLP, translation models, and Python.
What is a Multilingual Chatbot?
A multilingual chatbot is an AI-powered conversational agent that can interact with users in multiple languages. It can detect the user’s language, translate input if needed, process intent, and respond in the same language—all automatically.
Key skills include:
- Language detection
- Intent recognition
- Multilingual embeddings or translation
- Localized responses
- Context handling
Why Are Multilingual Chatbots Important?
Global Customer Support
Businesses can support users from different regions without hiring multilingual staff.
Improved User Satisfaction
Users prefer interacting in their native language, especially for support queries.
Cost Efficiency
One chatbot can replace dozens of monolingual bots or human agents.
Scalability
Adding a new language no longer requires building a new system.
How Multilingual Chatbots Work (Architecture)?
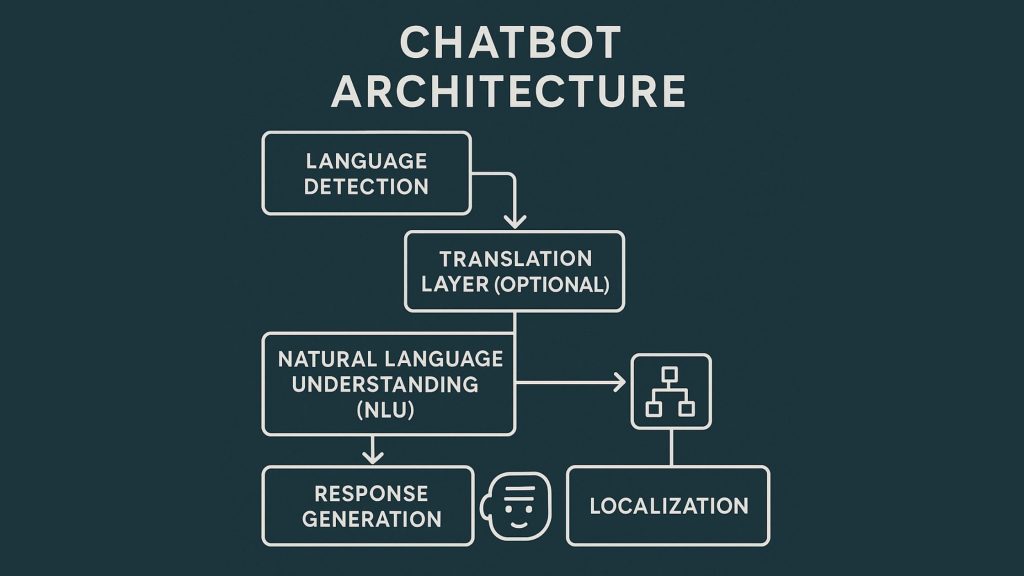
A typical multilingual chatbot includes:
Language Detection
Tools like langdetect, fastText, or LLM-based classifiers identify language instantly.
Translation Layer (Optional)
Some chatbots translate all input into a base language (usually English), process it, and then translate the output back.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
ML/NLP chatbot models extract entities, intents, and sentiments across languages.
Response Generation
Depending on design:
- Rule-based
- Template-based
- Generative AI (LLMs like GPT, Llama, Mistral)
Localization
Includes:
- Regional formatting (date, currency)
- Culturally relevant phrasing
- Language-specific grammar rules
How to Build a Multilingual Chatbot (With Python Code)?
Here’s a simple Python example using:
- langdetect for language detection
- googletrans for translation
- A mock response function (replace with your ML model)
Python Script: Basic Multilingual Chatbot Pipeline
from langdetect import detect
from googletrans import Translator
translator = Translator()
def chatbot_response(message):
# Dummy logic – replace with your NLP or LLM
return "Hello! How can I help you today?"
def multilingual_chatbot(user_input):
# Step 1: Detect language
user_lang = detect(user_input)
# Step 2: Translate to English
translated_input = translator.translate(user_input, dest='en').text
# Step 3: Process (your chatbot logic)
bot_reply = chatbot_response(translated_input)
# Step 4: Translate back to user's language
translated_reply = translator.translate(bot_reply, dest=user_lang).text
return translated_reply
# Example
print(multilingual_chatbot("Hola, necesito ayuda con mi factura"))
Output:
¡Hola! ¿Cómo puedo ayudarte hoy?This code demonstrates the core workflow: detect → translate → process → translate back.
Advanced Approaches
Multilingual Language Models
Instead of translation, you can use models trained across languages:
- XLM-RoBERTa
- mBERT
- Llama 3 multilingual variants
- Mistral-Nemo multilingual
These models create shared language embeddings, improving accuracy.
Fully Generative LLM-Based Chatbots
Modern LLMs are inherently multilingual and can:
- detect languages
- switch languages mid-conversation
- respond natively without translation
Offline Multilingual Chatbots
Using local models (e.g., GGUF Llama models) ensures privacy and lower costs.
Use Cases of Multilingual Chatbots
- Customer Support (Global SaaS companies)
- E-commerce Support
- Travel & Hospitality
- Healthcare Assistance in multiple languages
- Banking & Fintech
- Educational Platforms
Looking For a Multilingual Chatbot Tailored to Your Brand?
Let our team build a personalized chatbot tailored to your audience, languages, response style, and engagement goals.
Final Thoughts
A multilingual chatbot is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for global digital interactions. As LLMs and NLP improve, building multilingual bots becomes easier, faster, and more scalable. Whether you use translation, multilingual embeddings, or LLMs, the impact on customer experience is huge.