Cyber Security Vs Artificial Intelligence: Understanding the Core Differences
Blog Summary:
This guide covers the complete breakdown of Cyber Security Vs Artificial Intelligence, explaining how both differ in purpose, approach, and impact. It highlights how AI strengthens cyber security through predictive detection, automation, and intelligent analytics. You’ll also explore key challenges, future trends, and how BigDataCentric supports smarter, more resilient security systems.
The growing complexity of digital ecosystems has made security a top priority for every industry. As organizations rely more on data-driven operations, two major domains—cybersecurity and artificial intelligence—have become central to protecting and optimizing modern systems.
The comparison between these two fields, often framed as Cyber Security Vs Artificial Intelligence, highlights how they differ in purpose yet frequently work together to strengthen digital defenses.
Cybersecurity focuses on safeguarding networks, data, applications, and infrastructure from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, plays a broader role in technology by automating decision-making, analyzing large datasets, and enhancing processes across domains like healthcare, retail, finance, and more.
As cyber threats grow more advanced, organizations are increasingly integrating AI-powered techniques to improve detection, response, and risk management. From behavioral analysis to automated incident handling, this merging of the two fields is transforming traditional security practices and enabling more proactive protection.
Overview of Cyber Security
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting digital systems, networks, applications, and sensitive information from threats that compromise confidentiality, integrity, or availability. As organizations expand their digital presence across cloud platforms, connected devices, and online applications, the attack surface grows wider, making robust security measures essential.
Modern cybersecurity involves a combination of preventive and responsive strategies. Preventive measures include firewalls, encryption, identity and access management, and vulnerability assessments. Responsive mechanisms include incident detection, threat analysis, and mitigation efforts to minimize damage when an attack occurs.
Industries that rely heavily on data, such as ML in cybersecurity demonstrate how essential strong defensive frameworks have become in maintaining trust and operational continuity.
Cyber threats now range from ransomware and phishing to advanced persistent threats and supply chain attacks. Because these threats evolve rapidly, cybersecurity teams must continuously update policies, conduct security audits, and adopt advanced tools to identify suspicious behavior early.
This ongoing effort ensures organizations remain resilient in a landscape where digital risks have become increasingly sophisticated.
Overview of Artificial Intelligence in Technology
Artificial intelligence has become a foundational element in modern technology, enabling machines to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence. From pattern recognition and natural language understanding to decision-making and automation, AI supports a wide range of applications across industries.
Its growing influence can be seen in areas such as AI in product development, energy management, and intelligent automation, where data-driven insights enhance efficiency and innovation.
AI systems work by analyzing vast volumes of data, identifying patterns, and generating predictions or actions based on learned behavior. These capabilities allow businesses to streamline processes, personalize customer experiences, and optimize operations at scale.
Technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks enable AI models to adapt and improve continuously.
In technology ecosystems, AI strengthens everything from customer service chatbots to advanced data analytics platforms. It also plays a crucial role in real-time decision-making, enabling organizations to respond faster to changing environments.
Cyber Security vs Artificial Intelligence
Below is a clear, structured comparison table that explains how the two domains differ across key parameters.
| Factor | Cyber Security | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Core Purpose | Protects systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, breaches, and digital threats. | Enhances automation, decision-making, and data processing across technological applications. |
| Focus Area | Threat prevention, detection, and incident response. | Pattern recognition, prediction, optimization, and intelligent automation. |
| Approach to Problem-Solving | Primarily rule-based with predefined protocols and security policies. | Data-driven learning that improves accuracy and decision-making over time. |
| Data Dependency | Requires logs, security events, and system metadata to detect intrusions. | Relies heavily on large datasets to train models and make predictions. |
| Processing Method | Manual monitoring combined with automated tools for alert management. | Automated processing using machine learning and deep learning techniques. |
| Automation Level | Limited automation; human intervention remains crucial in many scenarios. | Highly automated, capable of independently analyzing and acting on data. |
| Adaptability | Responds based on known threat patterns and established security rules. | Continuously adapts and learns from new data to identify evolving patterns. |
| Threat Detection | Detects suspicious activities through signatures, rules, and anomaly checks. | Identifies threats using predictive models and behavioral analysis. |
| Response Time | Often depends on human analysts for verification and action. | Offers faster responses by automating detection and incident handling. |
| Human Intervention | High reliance on security teams to assess alerts and manage incidents. | Reduced dependency due to intelligent automation, though oversight is still required. |
| Integration with IT Systems | Integrated through traditional tools such as firewalls, SIEMs, and antivirus software. | Integrated through APIs, automation tools, and learning models across IT systems. |
How Artificial Intelligence is Transforming Cyber Security?
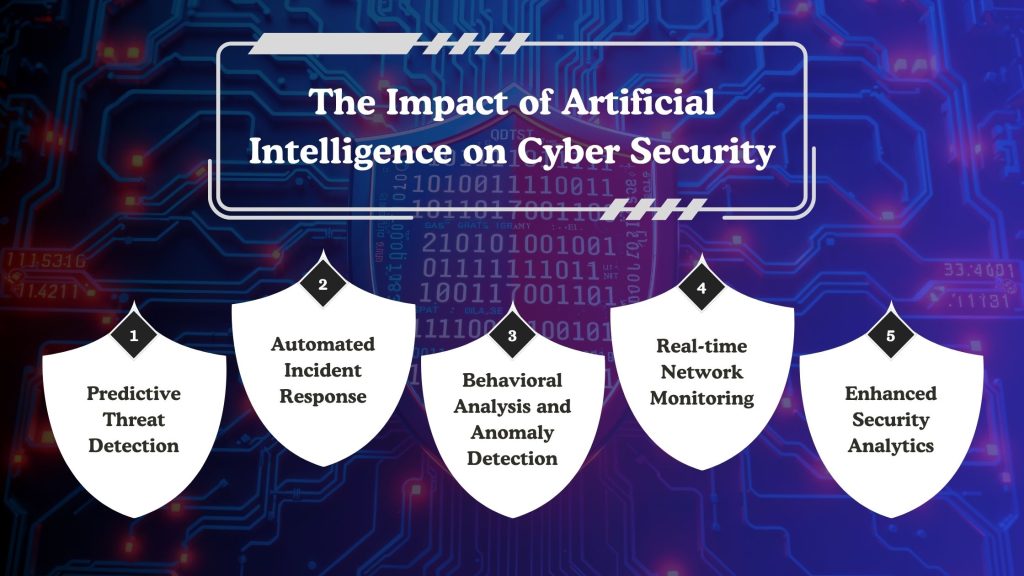
Artificial intelligence is reshaping defensive strategies by enabling systems to operate faster, with greater accuracy, and with greater adaptability. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations rely on AI-powered mechanisms to strengthen detection, automate incident handling, and analyze vast security datasets.
AI’s ability to learn from patterns, continuously monitor behavior, and respond proactively is reducing the burden on security teams while elevating overall protection. Below are the key areas where AI is transforming the cybersecurity landscape –
Predictive Threat Detection
AI models analyze historical attack patterns, network logs, and user behaviors to identify potential threats before they cause damage. By learning from large datasets, these models can predict malicious actions, detect early indicators of compromise, and flag emerging risks even when no signatures or rules exist.
This predictive capability allows organizations to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and reduces the chances of zero-day attacks slipping through traditional defenses.
Automated Incident Response
Incident response traditionally involves multiple manual steps—from identifying anomalies to verifying threats and implementing mitigation measures. AI automates much of this process by instantly categorizing alerts, isolating compromised systems, and initiating predefined remediation actions.
This level of automation significantly lowers response time and helps prevent the lateral movement of attacks. It also reduces human fatigue, enabling security teams to focus on high-priority cases rather than routine alert handling.
Behavioral Analysis and Anomaly Detection
One of the most impactful contributions of AI to cybersecurity is its ability to analyze normal user and system behavior over time. By establishing behavioral baselines, AI can detect unusual patterns such as unauthorized access attempts, abnormal login timings, risky transactions, or deviations in data usage.
This capability is especially beneficial for identifying insider threats or subtle attacks that bypass traditional tools. Industries leveraging data science in retail use similar behavioral insights to understand patterns, which now play a critical role in security monitoring as well.
Real-time Network Monitoring
AI enhances real-time visibility across networks by processing data streams continuously and identifying anomalies within milliseconds. This allows organizations to detect suspicious traffic, unusual communication patterns, or compromised devices as soon as they appear.
By leveraging advanced machine learning models to scan network activity at scale, organizations gain deeper insights into potential risks without relying solely on periodic manual monitoring.
Enhanced Security Analytics
Security operations generate massive volumes of data—from logs to event alerts—making it challenging to manually identify critical threats. AI strengthens security analytics by correlating events, highlighting hidden risks, and uncovering attack patterns that human analysts may miss.
It enhances SIEM platforms with intelligent filtering, risk scoring, and contextual insights, enabling faster decision-making and more accurate threat validation.
Enhance Your Enterprise Security Framework
Implement AI-powered monitoring and predictive threat detection to reinforce protection across your systems and operations.
Benefits of Integrating AI with Cyber Security

The combination of artificial intelligence and cyber security adds a proactive, adaptive, and scalable layer of defense to modern IT environments. As cyber threats evolve in speed and sophistication, AI-driven mechanisms help organizations detect anomalies earlier, respond faster, and strengthen their overall security posture.
Below are the key benefits of merging AI with cybersecurity practices –
Improved Threat Intelligence
AI enhances traditional threat intelligence by continuously analyzing global attack patterns, malware behavior, IP blacklists, and system logs. This provides organizations with deeper context on emerging threats, enabling quicker and more informed decisions.
AI-powered correlation also uncovers hidden risks that may not be visible through manual analysis.
Reduced False Positives
One of the major challenges in cybersecurity is the overwhelming number of false alerts that burden security teams. AI models learn from patterns and historical data to distinguish genuine threats from harmless anomalies.
By minimizing false positives, analysts can focus attention on real issues rather than sorting through noise.
Faster Detection and Resolution
AI monitors systems in real time, detecting suspicious activity within seconds. Automated workflows trigger immediate responses—such as isolating infected devices or blocking malicious IPs—significantly reducing dwell time.
Faster mitigation prevents attackers from expanding their reach and limits potential damage.
Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency
AI’s ability to process and analyze massive datasets improves the accuracy of threat identification. Machine learning models continuously refine themselves as new data arrives, improving precision over time.
This enhanced accuracy translates into more efficient security operations and reduces dependence on manual intervention.
Strengthened Data Protection
AI plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information by detecting unusual access patterns, enforcing data policies, and preventing unauthorized data movement. Its adaptability helps secure environments where data complexity continues to grow, just as structured frameworks in big data architecture require robust protection mechanisms.
Key Challenges in Cyber Security and Artificial Intelligence
While merging AI with cybersecurity unlocks numerous advantages, it also introduces unique challenges that organizations must address carefully. These challenges arise from data complexity, ethical concerns, evolving attack techniques, and integration limitations.
Below are the major challenges associated with the coexistence of AI and cybersecurity –
Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
AI systems require large datasets to learn effectively, but the use of sensitive information raises concerns around privacy, ownership, and ethical handling. In cybersecurity, this becomes even more critical because logs, user interactions, and access data may contain personal or confidential details.
Without strong governance frameworks and compliance measures, organizations risk violating privacy regulations.
Adversarial Attacks and Bias
AI systems can be manipulated through adversarial attacks, where small, undetectable changes are introduced to mislead the model. Attackers may intentionally poison training data or exploit algorithmic weaknesses to bypass security measures.
Additionally, if AI models learn from biased or incomplete datasets, their decisions may become inaccurate, leading to increased false negatives and misidentified threats.
Lack of Skilled Professionals
The rapid adoption of AI-driven cybersecurity tools has created a significant skills gap. Many organizations struggle to find professionals who understand both cyber defense and AI model development. This shortage delays implementation, limits optimization, and increases dependency on outsourced expertise.
A similar talent gap has been observed across fields like ML development companies, where specialized skills are essential for operational success.
Integration Complexity
Integrating AI into existing security frameworks often requires architectural changes, data restructuring, and workflow modifications. Legacy systems may not support advanced models, and real-time data pipelines may need upgrades to handle high processing demands.
These integration challenges slow down adoption and increase implementation costs.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
AI adoption in cybersecurity must align with various international standards and security regulations. Organizations must ensure that AI-driven processes meet compliance requirements related to transparency, audit trails, and data handling.
Failing to address regulatory obligations can lead to operational risks, penalties, and weakened trust.
Future Trends of Cyber Security and Artificial Intelligence
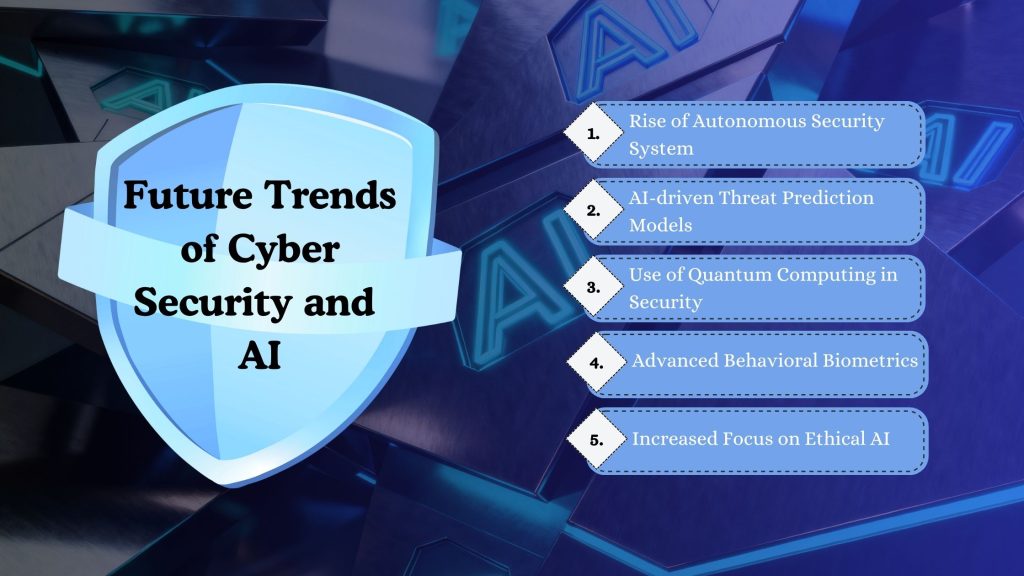
The relationship between cybersecurity and AI is evolving rapidly, shaping the future of digital defense systems. As organizations face increasing data volumes and sophisticated cyber threats, upcoming advancements will redefine how threats are detected, analyzed, and mitigated.
Below are the key future trends that will influence how both domains work together in the coming years –
Rise of Autonomous Security Systems
Autonomous systems capable of identifying, analyzing, and responding to threats without human intervention will become more common. These systems will leverage continuous learning to update themselves, enabling organizations to build dynamic, self-defending networks.
As the gap widens between traditional methods and AI-driven capabilities, autonomous security will play a defining role in strengthening protection frameworks.
AI-driven Threat Prediction Models
Prediction will move beyond identifying known risks to understanding attacker behavior, anticipating exploit paths, and forecasting vulnerabilities before they are weaponized.
These models will significantly reduce reaction time, supporting scalable, proactive approaches—a necessity highlighted across sectors that leverage predictive capabilities.
Use of Quantum Computing in Security
Quantum computing holds the potential to disrupt cybersecurity by breaking traditional encryption methods while simultaneously enabling more advanced cryptographic techniques.
Integrating AI with quantum algorithms will enable faster threat detection, improved encryption algorithms, and more sophisticated simulation capabilities. However, it will also require a rethinking of security architectures to remain resistant to quantum-era attacks.
Advanced Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics powered by AI—such as typing patterns, mouse movements, voice recognition, and gaze tracking—will become core components of authentication systems. Unlike static passwords, these dynamic behaviors are harder to replicate, offering stronger identity verification.
This trend supports a shift toward frictionless yet secure access management for digital ecosystems.
Increased Focus on Ethical AI
As AI becomes deeply embedded in cybersecurity operations, ethical considerations will gain more attention. Transparent algorithms, unbiased data use, and responsible automation will be essential for maintaining trust.
Regulatory bodies will also enforce stricter guidelines, requiring organizations to adopt explainable AI models and ensure accountability across automated decision-making.
How BigDataCentric Can Help with AI-driven Cyber Security Solutions?
BigDataCentric delivers advanced, intelligence-powered cybersecurity solutions designed to help businesses stay ahead of evolving digital threats. With strong expertise across areas like big data security and AI in digital transformation, the company builds security frameworks that combine automation, predictive analytics, and real-time monitoring.
BigDataCentric integrates AI-driven capabilities into existing security infrastructures to improve threat visibility, reduce response time, and enhance overall accuracy. The team focuses on predictive security models that identify risks early, enabling organizations to prevent breaches before they escalate.
Intelligent analytics further strengthen detection by uncovering hidden patterns, correlating events, and providing deeper context for potential vulnerabilities.
BigDataCentric also reinforces data protection through intelligent monitoring and adaptive controls. These solutions scale smoothly across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid ecosystems, allowing businesses to strengthen their security posture without extensive infrastructure changes.
By combining AI-driven insights with deep technical expertise, BigDataCentric helps organizations build resilient, future-ready security systems that tackle modern cyber challenges with confidence.
Confused About How AI Can Improve Your Cybersecurity Framework?
Smart analytics and predictive models make your systems more resilient against evolving threats.
Conclusion
The comparison of Cyber Security Vs Artificial Intelligence shows that while both fields serve different core purposes, their convergence is reshaping how modern digital systems are protected.
Cybersecurity remains essential for safeguarding networks, data, and infrastructure, while AI adds a proactive, adaptive layer that enhances detection, speeds response times, and strengthens overall resilience. With the rise of advanced analytics, prediction models, and intelligent automation, organizations can address threats with far greater accuracy and efficiency.
As businesses continue adopting innovative technologies—similar to trends seen in intelligent automation—integrating AI into cybersecurity will no longer be optional. It will become a critical step toward building self-defending, future-ready ecosystems.
By strategically embracing this combination, companies can stay ahead of evolving risks and maintain strong digital trust.
FAQs
-
Will AI replace cyber security?
No, AI will not replace cyber security. It enhances detection and automation, but human expertise is still required for decision-making, handling complex threats, and ensuring ethical, accurate deployment.
-
How are AI technologies used to detect cyber threats?
AI analyzes patterns, monitors behavior, and identifies anomalies in real time. It detects suspicious activities faster than manual methods and flags potential risks before they escalate.
-
Can AI prevent ransomware and phishing attacks?
Yes, AI can help prevent ransomware and phishing by detecting unusual access attempts, scanning malicious patterns, and identifying fraudulent communication indicators before they reach users.
-
Is AI suitable for cloud security?
Absolutely. AI strengthens cloud security through continuous monitoring, automated threat detection, and intelligent access control, making cloud environments more secure and resilient.

About Author
Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
ToggleHere's what you will get after submitting your project details:
- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
Our Offices
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




