
Rapid Elasticity in Cloud Computing: Key Insights and Examples

Blog Summary:
This guide explains the concept of rapid elasticity in cloud environments and how it enables on-demand resource scaling. It covers how elasticity works, its types, real-world use cases, benefits, challenges, and how it differs from scalability. The article also highlights how major cloud providers implement elasticity to support modern, dynamic workloads.
Cloud environments are no longer built to handle just predictable workloads. Modern applications face sudden traffic spikes, seasonal demand, and usage patterns that can change within minutes. In such scenarios, static infrastructure planning often leads to wasted resources or performance bottlenecks. This is where rapid elasticity in cloud computing becomes a critical thing rather than a nice-to-have feature.
Rapid elasticity allows cloud environments to automatically scale resources up or down in response to real-time demand. Instead of provisioning infrastructure for peak usage at all times, businesses can dynamically adjust compute, storage, and network capacity as needed. This flexibility helps organizations maintain performance during high-demand periods.
As digital products become more customer-facing and data-intensive, rapid elasticity plays a central role in ensuring application stability, cost control, and operational efficiency. From online retail platforms that handle flash sales to SaaS products that onboard thousands of users overnight, elasticity has become a foundational pillar of modern cloud architecture.
In the sections ahead, we’ll explore what rapid elasticity means in practice, how it works behind the scenes, its different types, real-world use cases, benefits, challenges, and how major cloud providers implement it.
What is Rapid Elasticity in Cloud Computing?
Rapid elasticity is the ability of a cloud environment to automatically and quickly adjust computing resources in response to real-time demand. This adjustment can happen in minutes—or even seconds—without manual intervention.
Resources such as virtual machines, storage, memory, and bandwidth can be provisioned or released as workload requirements change.
In practical terms, rapid elasticity in cloud computing ensures that applications always have access to the right amount of infrastructure at the right time. When demand increases, additional resources are allocated instantly.
When demand drops, excess resources are scaled back just as quickly. This dynamic behavior differentiates cloud platforms from traditional on-premises systems, where capacity planning is rigid and time-consuming.
A key characteristic of rapid elasticity is that scaling appears virtually unlimited to the user. Organizations are not constrained by the availability of physical hardware or by procurement delays. Instead, cloud providers maintain large resource pools that can be shared and reassigned across multiple customers on demand.
Another important aspect is automation. Scaling decisions are typically driven by predefined policies, performance thresholds, or real-time metrics such as CPU usage, request volume, or memory consumption. This automation minimizes human involvement and reduces the risk of delayed responses during traffic spikes.
To put it simply, rapid elasticity allows businesses to stay responsive, cost-aware, and performance-driven in unpredictable environments—making it one of the most defining features of cloud-based infrastructure.
How Rapid Elasticity Works?
Rapid elasticity continuously monitors application workloads and system performance in real time. Cloud platforms track metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, traffic volume, and request rates to understand when resource demand increases or decreases.
When predefined thresholds are reached, automated scaling mechanisms are triggered. These mechanisms provide additional resources during periods of high demand or release unused resources when workloads drop. Because infrastructure is virtualized and pooled, these adjustments happen quickly without manual intervention.
Policy-based controls guide this process by defining how and when scaling should occur. Businesses can prioritize performance, availability, or cost efficiency, ensuring that cloud computing adapts to both technical and operational requirements.
Types of Rapid Elasticity in Cloud Computing
Rapid elasticity can be implemented in multiple ways, depending on how resources are scaled. Each type addresses different workload patterns and performance needs, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable approach for their applications:
Vertical Elasticity (Scaling Up/Down)
Vertical elasticity involves increasing or decreasing the capacity of a single resource, such as adding more CPU, memory, or storage to an existing virtual machine. This approach is useful when applications need more power without changing their overall architecture. However, scaling limits are tied to the maximum capacity of a single instance.
Horizontal Elasticity (Scaling Out/In)
Horizontal elasticity focuses on adding or removing multiple instances to distribute workloads. When demand rises, new instances are created; when it falls, excess instances are terminated. This method is widely used in cloud rapid elasticity because it supports high availability and handles large traffic spikes more effectively.
Burstable Elasticity
Burstable elasticity allows systems to temporarily exceed normal resource limits during short-term spikes. This type is ideal for unpredictable workloads, such as flash sales or sudden surges in user activity. Once the demand normalizes, resources automatically return to their baseline levels.
Benefits of Rapid Elasticity in Cloud Computing
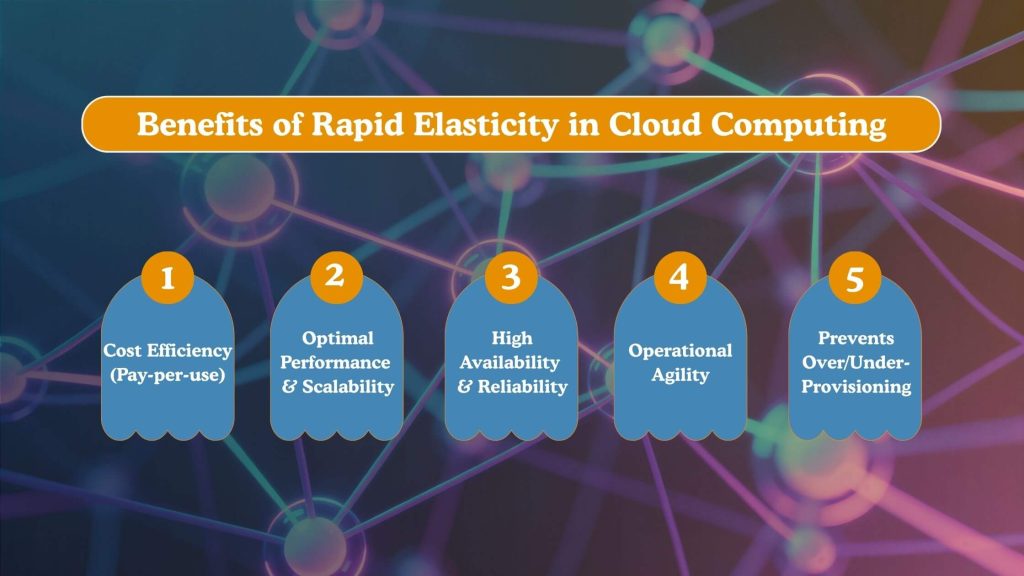
Rapid elasticity delivers measurable advantages by aligning infrastructure usage with real-time demand. Instead of relying on fixed capacity planning, businesses gain the flexibility to scale resources precisely when needed, improving both performance and cost control.
Cost Efficiency (Pay-Per-Use)
With rapid elasticity cloud services, organizations pay only for the resources they consume. Infrastructure scales down automatically during low-usage periods, reducing idle costs and eliminating the need for large upfront hardware investments.
Optimal Performance & Scalability
Elastic resource allocation ensures applications maintain consistent performance even during traffic spikes, particularly in environments built on scalable big data architecture that must process large volumes of data in real time.
High Availability & Reliability
Rapid elasticity helps maintain service continuity by distributing workloads across multiple resources. If demand surges or a component fails, additional resources can be activated instantly to preserve availability.
Operational Agility
Teams can respond faster to changing business needs without manual provisioning. This agility allows quicker launches, updates, and experimentation while keeping infrastructure aligned with workload demands.
Prevents Over/Under-Provisioning
By scaling resources up or down in real time, cloud rapid elasticity prevents both resource shortages and unnecessary excess capacity. This balance improves efficiency and supports smarter infrastructure planning.
Looking to Optimize Cloud Costs and Performance?
We help businesses design cloud solutions that balance rapid scaling, reliability, and cost efficiency across dynamic workloads.
Key Use Cases of Rapid Elasticity
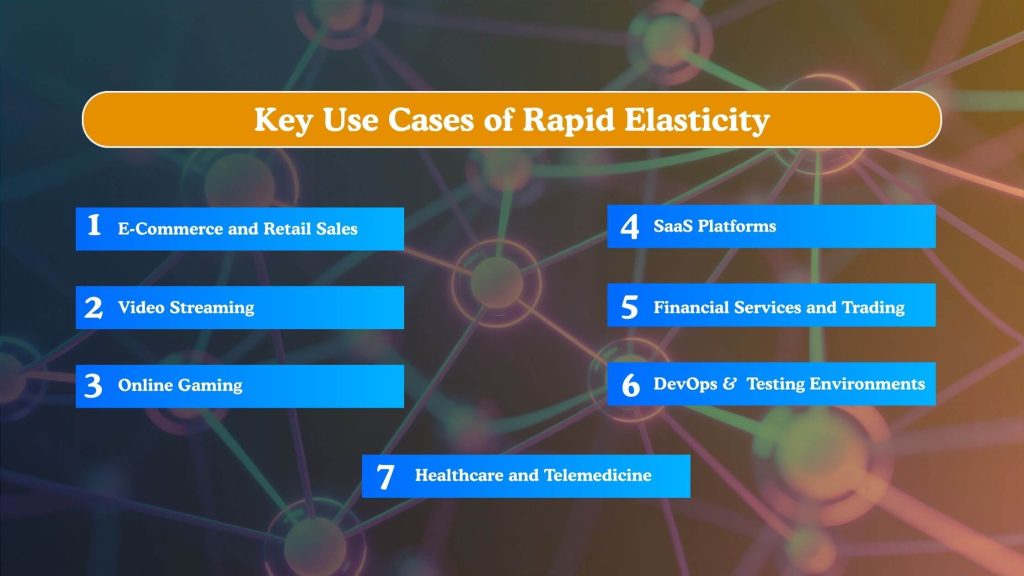
Rapid elasticity is especially valuable in industries where demand fluctuates frequently or unpredictably. By dynamically adjusting resources, organizations can maintain performance, control costs, and deliver uninterrupted services across diverse workloads.
E-Commerce and Retail Sales
Online retail platforms often experience sudden traffic surges during sales events, festive seasons, or product launches. Rapid elasticity enables infrastructure to scale instantly to support increased user activity and high transaction volumes. This ensures checkout processes remain stable and responsive even during peak demand periods.
Video Streaming and Content Delivery
Streaming platforms rely on cloud computing elasticity to manage fluctuating viewer demand throughout the day. During live events or new content releases, resources automatically scale to support high concurrent users. This helps maintain smooth video playback and consistent content delivery without interruptions.
Online Gaming
Multiplayer and cloud-based games face unpredictable usage spikes during peak hours or new game launches. Rapid elasticity allows gaming platforms to scale compute and network resources dynamically. This helps reduce latency, prevent server overloads, and deliver a seamless gaming experience.
SaaS Platforms (Software as a Service)
SaaS applications must handle varying user loads, feature rollouts, and onboarding spikes. Rapid elasticity cloud services allow these platforms to scale resources in real time without affecting application performance. This flexibility supports growth while keeping operational costs under control.
Financial Services and Trading
Financial platforms process high volumes of transactions, especially during market volatility. Rapid elasticity ensures systems can scale instantly to handle increased trading activity. This capability helps maintain transaction accuracy, speed, and system reliability under pressure.
DevOps and Testing Environments
Development and testing environments are often temporary and resource-intensive. Rapid elasticity allows teams to provision infrastructure quickly for testing, CI/CD pipelines, and simulations. Once tasks are completed, resources can be released to avoid unnecessary costs.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
Telemedicine platforms and digital health systems experience spikes in demand during emergencies or peak consultation hours. Rapid elasticity enables these platforms to scale securely and reliably. This ensures uninterrupted access to virtual care services and patient data.
You Might Also Like:
Rapid Elasticity vs Scalability
While rapid elasticity and scalability are closely related concepts, they are not the same. Scalability focuses on the system’s ability to handle growth over time, whereas rapid elasticity emphasizes how quickly and automatically resources can be adjusted in response to changing demand. The table below clearly highlights the key differences:
| Aspect | Rapid Elasticity | Scalability |
|---|---|---|
| Core Meaning | Automatic and immediate adjustment of resources based on demand | The ability of a system to handle an increased workload by adding resources |
| Speed of Adjustment | Near real-time or on-demand | Usually planned and gradual |
| Automation Level | Highly automated with minimal manual intervention | Can be manual or automated |
| Resource Allocation | Resources are provisioned and released dynamically | Resources are added and generally remain allocated |
| Cost Impact | Optimizes costs through pay-per-use | May lead to long-term resource commitment |
| Typical Use Case | Handling sudden traffic spikes or short-term demand | Supporting long-term business growth |
| Example Scenario | Flash sales, live events, sudden user surge | Expanding infrastructure for a growing user base |
In short, elasticity and scalability are not mutually exclusive; you can choose both. Most modern cloud architectures rely on both scalability to support long-term expansion and rapid elasticity to efficiently manage short-term, unpredictable workload fluctuations.
Challenges and Limitations of Rapid Elasticity
While rapid elasticity offers significant flexibility and efficiency, it also introduces certain challenges that organizations must manage carefully. Without proper controls and planning, elastic environments can become complex and difficult to optimize.
Cost Unpredictability
Although pay-per-use pricing is a major advantage, rapid scaling can sometimes lead to unexpected costs. Sudden spikes in resource consumption may increase cloud bills if usage is not closely monitored or capped through policies.
Monitoring and Governance Complexity
Elastic environments require continuous monitoring to track performance, usage, and compliance. Managing scaling rules, alerts, and access controls across dynamically changing resources can add governance complexity, especially in large cloud deployments.
Performance Tuning Issues
Frequent scaling events may introduce performance variations if applications are not designed to handle dynamic resource changes. Without proper optimization, scaling actions can impact response times or application stability during peak periods.
Rapid Elasticity Application to Cloud Service Providers
Major cloud providers embed rapid elasticity directly into their core services, enabling businesses to scale resources automatically while maintaining performance and reliability. Each provider implements elasticity using its own tools, policies, and infrastructure capabilities:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services offers rapid elasticity through features like auto scaling and managed compute services. These tools allow applications to scale resources automatically based on traffic patterns, performance metrics, or custom rules. This approach supports both short-term demand spikes and steady workload changes without manual intervention.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure implements elasticity using services such as virtual machine scale sets and platform-managed scaling. Azure enables applications to adjust capacity dynamically while maintaining availability across regions. This makes it suitable for enterprises running complex, distributed workloads.
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform focuses on automated, metrics-driven scaling across compute and container-based services. Its elasticity capabilities allow workloads to respond quickly to real-time demand, supporting high-performance applications with minimal operational overhead.
Future Outlook of Rapid Elasticity in Cloud Computing
Rapid elasticity is expected to evolve further as cloud platforms become more intelligent and autonomous. With growing application complexity and unpredictable usage patterns, elasticity will play an even more critical role in maintaining performance and cost efficiency.
Increased Automation
Future cloud environments will rely more heavily on automated decision-making. Scaling actions will increasingly be driven by predictive analytics rather than reactive thresholds, enabling systems to prepare for demand changes before they occur.
Smarter Resource Optimization
Advancements in workload analysis and resource scheduling will allow cloud platforms to optimize resource usage more precisely. This will help reduce waste, improve performance consistency, and align infrastructure consumption more closely with business objectives.
Greater Adoption Across Industries
As digital transformation accelerates, more industries will adopt elastic cloud architectures. From manufacturing to education and public services, rapid elasticity will enable scalable, resilient systems that adapt to evolving operational needs.
Planning a Scalable Cloud Architecture?
Discuss your cloud requirements with our experts and design an infrastructure that adapts instantly to changing workloads and business demands.
Conclusion
Rapid elasticity has become a defining capability of modern cloud environments, enabling businesses to respond instantly to fluctuating workloads without compromising performance or cost efficiency. By dynamically scaling resources up or down, organizations can maintain application stability, improve user experience, and avoid the risks of over- or under-provisioning.
As cloud adoption continues to grow, rapid elasticity in cloud computing will remain essential for handling unpredictable demand across industries such as e-commerce, healthcare, finance, and SaaS. When combined with scalability, monitoring, and automation, elasticity helps build resilient systems that support both short-term spikes and long-term growth.
At BigDataCentric, cloud solutions are designed with elasticity at the core—ensuring workloads remain responsive, cost-optimized, and performance-driven. By aligning elastic cloud architectures with data-driven insights, Big Data Centric helps organizations design, optimize, and manage cloud environments that adapt seamlessly to real-world business demands.
FAQs
-
What are the 5 key features of cloud computing?
The five key features are on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. Together, they enable scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient use of cloud resources.
-
What are the core elements of elasticity in the cloud?
The core elements include real-time monitoring, automated scaling, resource virtualization, and policy-based controls. These components enable cloud systems to dynamically adjust resources based on workload demand.
-
What is the difference between rapid elasticity and scalability?
Rapid elasticity focuses on how quickly resources can be scaled up or down automatically, often in real time. Scalability refers to a system’s ability to grow and handle increased workloads over the long term.
-
What is a real-life example of elasticity?
An e-commerce platform that scales its infrastructure during a flash sale and then scales it back after the sale ends is a real-life example of elasticity. Resources are adjusted automatically based on user traffic.
-
What are the 4 C's of cloud security?
The four C’s of cloud security are compliance, confidentiality, control, and continuity. They focus on meeting regulations, protecting data, managing access, and ensuring service availability.

About Author
Jayanti Katariya is the CEO of BigDataCentric, a leading provider of AI, machine learning, data science, and business intelligence solutions. With 18+ years of industry experience, he has been at the forefront of helping businesses unlock growth through data-driven insights. Passionate about developing creative technology solutions from a young age, he pursued an engineering degree to further this interest. Under his leadership, BigDataCentric delivers tailored AI and analytics solutions to optimize business processes. His expertise drives innovation in data science, enabling organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Table of Contents
ToggleHere's what you will get after submitting your project details:
- A strict non-disclosure policy.
- Get in discuss with our experts.
- Get a free consultation.
- Turn your idea into an exceptional app.
- Suggestions on revenue models & planning.
- No obligation proposal.
- Action plan to start your project.
- We respond to you within 8 hours.
- Detailed articulate email updates within 24 hours.
Our Offices
USA
500 N Michigan Avenue, #600,Chicago IL 60611




